Resumen
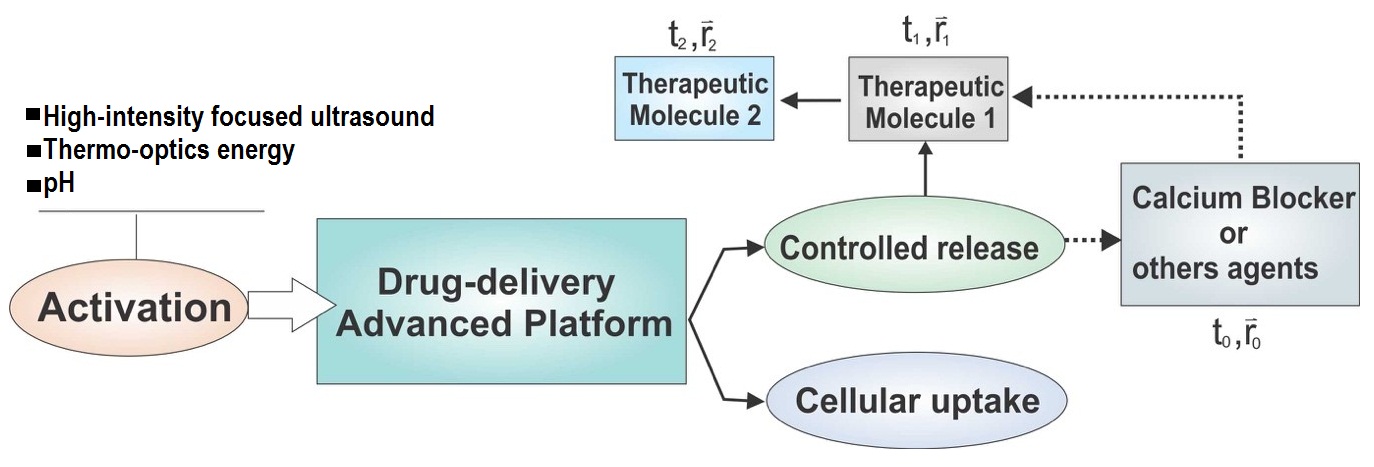
A partir de nanocajas metálicas de doble pared con un monoporo (DWSPNb) sintetizadas por efecto Kirkendall y reemplazo galvánico, se propone una plataforma multifuncional nanoestructurada con capacidad de liberación secuencial de agentes moleculares para uso terapéutico. La evaluación de la plataforma propuesta se hizo mediante cálculo numérico basado en las dimensiones, morfología y composición de las nanocajas sintetizadas. Para las combinaciones de dos moléculas farmacológicas de interés, se determinaron los coeficientes de difusión en función de la distancia a las paredes de la nanocaja y la concentración. La simulación realizada para la liberación de las dos moléculas de la cavidad interna a través del nanocanal formado entre las dos paredes de la nanocaja evidenció la cinética secuencial requerida. Este comportamiento permite programar entregas controladas en tiempo y lugar para reducir la resistencia a los fármacos duales y, consecuentemente, optimizar la dosis necesaria y evitar los efectos secundarios derivados. La composición metálica convirtió la nanocaja en una nanoantena optotérmica, lo que permite controlar la liberación y entrega de la carga molecular a través de polímeros sensibles a la temperatura, además de su uso potencial para tratamientos fotodinámicos y diagnósticos por imagen.
Referencias
Ahyja, G., Pathak, K. (2009). Porous Carriers for Controlled/Modulated Drug Delivery. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2, 599-607. DOI: 10.4103/0250-474X.59540
Augustine, R., Hasan, A., Primavera, R., Wilson, R., Thakor, A., Kevadiya, D. (2020). Cellular uptake and retention of nanoparticles: Insights on particle properties and interaction with cellular components. Materialstoday Communications, 25, 101692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101692
Aziz, G., Patarroyo, J., Parramon, S., Arenal, Raul., Duchamp, M., González, E., Henrard, L., Bastús, N., Dunin, R., Puntes, V., Arbio, J. (2016). Tuning the plasmonic response up: Hollow cuboid metal nanostructures. ACS Photonics, 3 (5), 770-779. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acsphotonics.5b00667
Bruno, G., Trani, N., Hood, R., Zabre, (2018). Unexpected behaviors in molecular transport through size-controlled nanochannels down to the ultra-nanoscale. Nature Communications,9, 1682. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04133-8
Buyl, P. (2018). Tidynamics: A tiny package to compute the dynamics of stochastic and molecular simulations. Journal of Open-Source Software, 3 (28), 877.
Cao, M., Wang, M., Gu, N. (2009). Optimized surface plasmon resonance sensitivity of gold nanoboxes for sensing applications. Journal Physics Chemical C, 113(4), 1217-1221. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp808000x
Carnovale, C., Bryant, G., Shukla, R., Bansal, V. (2016). Size, shape and surface chemistry of nano-gold dictate its cellular interactions, uptake and toxicity. Progress in Materials Science, 83, 152-190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2016.04.003
Calandrini, V., Pellegrini, E., Calligari, P., Hinsen, K., Kneller, G. R. (2011). NMoldyn-Interfacing Spectroscopic Experiments, Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Models for Time Correlation Functions. Collection SFN, 12, 201-232. DOI:10.1051/sfn/201112010
Chen, Z., Li, B., Xie, X., Zeng, F., Wu, S. (2018). A sequential enzyme-activated and light-triggered pro-prodrug nanosystem for cancer detection and therapy. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 6, 2547-2556. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB01989K
Cho, H., Kwon, G. (2011). Polymeric Micelles for Neoadjuvant Cancer Therapy and Tumor-Primed Optical Imaging. ACS Nano, 5, 8721-8729. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn202676u
Deirram, N., Zhang, Ch., Kermaniyan, S., Johnston, A., Such, G. (2019). pH-Responsive Polymer Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Macromolecular Rapid Communicatios, 40, 1-23.https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.201800917
Esquivel, R., Canale, I., Ramirez, M., Hernández, P., Zavala, P., Álvarez, E., Acuña, A. (2017).Nanobarras de oro recubiertas de poli(N-isopropilacrilamida) mediadas por una capa de quitosano tiolado: sensibilidad al pH térmico y propiedades ópticas. e-Polymers, 18, 163-174. https://doi.org/10.1515/epoly-2017-0135
Fievet, F., Langier, J., Blim, B., Beaudoin, B., Figlarz. (1989). Homogeneous and heterogeneous nucleations in the polyol process for the preparation of micron and submicron size metal particles. Solid State Ionics, 32, 198-205.
Gibson, J., Khanal, B., Zubarev, R. (2007). Paclitaxel-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles. Journal of the American Chemistry Society, 129, 11653.
Gonzalez, E., Arbiol, J., Puntes, V. (2011). Carving at the nanoscale: Sequential galvanic exchange and Kirkendall growth at room temperature. Science, 334, 1377-1380. DOI: 10.1126/science.1212822
Gonzalez, E., Puntes, V. Casals, E. (2015). Nanomateriales: Nanopartículas Coloidales. Nanocitec, Bogotá.
Gonzalez, E. (2016). Control de la superficie y el volumen en la nanoescala para la configuración y el diseño de nanodispositivos. Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas Fisicas y Naturales, 40 (157), 590-599. https://doi.org/10.18257/raccefyn.398
Gonzalez, E., Gil, E., Castro, C., Téllez, N., Riberos, T., González, F. (2008). Citotoxicidad in vitro de células tumorales con nanotubos de carbono de pared simple funcionalizados con polisulfónico M-aminobenceno y con polietilenglicol. Universitas Medica, 49, 317-327.
Hamada, H., Ishihara, K., Masuoka, N., Mikuni, K., Nakajima, N. (2006). Enhancement of watersolubility and bioactivity of paclitaxel using modified cyclodextrins. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 102, 369-371.
Han, J., Fu, J., Schoch, R. (2008). Molecular sieving using nanofilters: past, present and future. Lab on a Chip, 8(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.1039/B714128A
Harrell, C., Kohli, P., Siwy, Z., Marti,n C. (2004). DNA-Nanotube artificial ion channels. Journal of the American Chemistry Society, 126(48), 15646-15647.
Holt, J. K., Park, H., Wang, Y., Stadermann, M., Artyukhin, A., Grigoropoulos, C., Noy, A., Bakajin, O. (2006). Fast mass transport through sub-2-nanometer carbon nanotubes. Science, 312, 1034-1037.
Karniadakis, G., Beskok, A., Aluru, N. (2005). Microflows and Nanoflows: Fundamentals and Simulation, Springer, New York.
Kim, J., Piao, Y., Hyeon, T. (2009). Multifunctional nanostructured materials for multimodal imaging, and simultaneous imaging and therapy. Chemical Society Reviews Journal, 38, 372-390. DOI https://doi.org/10.1039/B709883A
Kojic, M., Milosevic, M., Kojic, N., Ferrari, M., Ziemys, A. (2011). On diffusion in nanospace.Journal of the Serbian Society for Computational Mechanics, 5(1), 104-118.
Konno, T., Watanabe, J., Ishiara, K. (2003). Enhanced solubility of paclitaxel using watersoluble and biocompatible 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine polymers. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 65, 209-214. DOI:10.1002/jbm.a.10481
Li, N., Zhang, P., Huang, C., Song, Y., Garg, S., Luan, Y. (2015). Co-delivery of doxorubicin hydrochloride and verapamil hydrochloride by pH-sensitive polymersomes for the reversal of multidrug resistance. RCS Advances, 5, 77986-77995. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA15313A
Li, W., Cai, X., Kim, C., Sun, G, Zhang, Y., Deng, R., Yang, M., Chen, J., Achilefu, S., Wang,L., Xia, Y. (2011). Gold nanocages covered with thermally-responsive polymers for controlled release by high-intensity focused ultrasound. Nanoscale, 3(4), 1724-1730. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0NR00932F
Mahmound, M., Snyder, B., ANDEl-Sayed, M. (2010). Surface Plasmon Fields and Coupling in the Hollow Gold Nanoparticles and Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Theory and Experiment. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 114, 74367443. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9109018
Maginn, E. J., Messerly, R. A., Carlson, D. J.; Roe, D. R., Elliott, J. R. (2019). Best Practices for Computing Transport Properties 1. Self-Diffusivity and Viscosity from Equilibrium Molecular Dynamics. Living Journal of Computational Molecular Science, 1(1), 6324. DOI:https://doi.org/10.33011/livecoms.1.1.6324
Malone, D., Anderson, J. (1978). Hindered diffusion of particles through small pores. Chemical Engineering Science, 33, 1429-1440. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(78)85192-6
Maji, S., Cesur, B., Zhang, Z., De Geest, B., Hoogenboom, R. (2016). Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)coated gold nanoparticles as colourimetric temperature and salt sensors. Polymer Chemistry, 7, 1705-1710. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5PY01959A
Mitchell, M., Billingsley, M., Haley, R., Wechsler, M., Peppas, N., Langer, R. (2020). Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 20, 101-124. DOI: 10.1038/s41573-020-0090-8
Mohammadi, M., Salami, M., Mamaqani, H., Golshan, M. (2017). Synthesis and investigation of dual pH- and temperature-responsive behaviour of poly[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate]-grafted gold nanoparticles. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 31, e3702.https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.3702
Morton, S., Lee, M., Dend, A., Dreaden, E., Siouve, E., Shopsowitz, K., Shah, N., Yaffe, M.,Hammoun, P. (2014). A Nanoparticle-Based Combination Chemotherapy Delivery System for Enhanced Tumor Killing by Dynamic Rewiring of Signaling Pathways. Science Signaling,7 (325), 44. Doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2005261
Nakamura, J., Nakajima, N., Matsumura, K and Hyo, S-H. (2010). Water-soluble Taxol Conjugates with Dextran and Targets Tumor Cells by Folic Acid Immobilization. Anticancer Research, 30, 903-909.
Niaz, S., Forbes, B. And Raimi-Abrahan, T. (2022). Exploiting Endocytosis for Non-Spherical Nanoparticle Cellular Uptake. Nanomanufacturing, 2, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing2010001
Ofridam, F., Tarhini, M., Lebaz, N., Gagnière, É., Mangin, D., Elaissari, A. (2021). pH-sensitive polymers: Classification and some fine potential applications. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 32, 1455-1484. DOI:10.1002/pat.5230
Palanikumar, L., Jeena, M., Kim, K., Oh, J., Kin, C., Park., Ryu, J.H. (2017). Spatiotemporally and SequentiallyControlled Drug Release from Polymer Gatekeeper–Hollow Silica Nanoparticles. Scientific Reports, 7, 46540. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46540
Parak, J. W. (2011). Complex colloidal assembly. Science, 334, 1359-1360. DOI: 10.1126/science.1215080
Price, E., Gesquiere, A. (2019). An in vitro assay and artificial intelligence approach to determine rate constants of nanomaterial-cell interactions. Scientific Reports, 9, 13943. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-50208-x
Punfa, W., Suzuki, S., Pitchakarn, P., Yodkeeree, S., Naiki, T., Takahashi, S., Limtrakul, P.(2014). Curcumin-loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Conjugated with Anti- P-glycoprotein Antibody to Overcome Multidrug Resistance. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, 15, 9249-9258. DOI: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.21.9249
Qiu, J., Liu, Y., Xia, Y. (2021). Radiolabeling of Gold Nanocages for Potential Applications in Tracking, Diagnosis, and Image-Guided Therapy. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 10, 1-11.
Qui, J., Xie, M., Wu, T., Qin, D., Xia, Y. (2020). Gold nanocages for effective photothermal conversion and related applications. Chemical Science, 11, 12955-12973.
Sadeghi, M., Jeon, S., Kwon, H-J. (2019). Enhancing Thermal Effect of Focused Ultrasound Therapy Using Gold Nanoparticles. IEEE Transaction NanoBioscience. DOI 10.1109/TNB.2019.2937327
Sanzari, I., Buratti, E., Huang, R., Tusan, C., Dinelli, F., Evans, N., Prodromakis, T., Bertoldo, M. (2020). Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) based thin microgel films for use in cell culture applications. Scientific Reports, 10, 6126. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-63228-9
Thomas, J. and McGaughey, A. (2009). Water flow in carbon nanotubes: transition to subcontinuum transport. Physics Review Letters, 102, 184502.
Thomas, J., Rja, R. (2012). Nanopore and nanoparticle catalysts. Chemical Records, 1(6), 448-466.
Vines, J., Yoon, J-H., Ryu, N-E., Lim, D.J., Park, H. (2019). Gold nanoparticles for phototermal cancer therapy. Frontiers in Chemistry, 7, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00167
WHO. (2022) Cancer, https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer, consulted 10 February 2022.
Xu, W., Thapa, R., Liu, D., Nissen, T., Granroth, T., Narvanen, A., Suvanto, M., Santos, H., Lehto, V. (2015). Smart porous silicon nanoparticles with polymeric coatings for sequential combination therapy. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 12, 4038-4047. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00473
Yao, Y., Zhou, Y., Liu, L., Xu, Y., Chen, Q., Wnag, Y., Wu, S., Deng, Y., Zhang, J., Shao, A. (2020). Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy and Its Role in Overcoming Drug Resistance. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 7, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2020.00193
Yu, j., Feliciano, T., Li, W., Lee, A., Odom, T. (2018). Gold nanoparticle size and shape effects on cellular uptake and intracellular distribution of siRNA nanoconstruct. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 28(6), 1791-1800. Doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.7b00252
Zhao, D., Yang, N., Wei, Y., Jin, Q., Want, Y., He, Y., Yang, Y., Han, B., Zhang, S., Wnag, D. (2020). Sequential drug release via chemical diffusion and physical barriers enabled by hollow multishelled structures. Nature Communication, 11, 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18177-2
Zhu, F., Tan, G., Zhong, Y., Jian, Y., Cai, L., Yu, Z., Liu, S., Ren, F. (2019). Smart nanoplatform for sequential drug release and enhanced chemo‑thermal effect of dual drug loaded gold nanorod vesicles for cancer therapy. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 17, 44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-019-0473-3
Ziemys, A., Grattoni, A., Fine, D., Hussain, F., Ferrari, M. (2010). Confinement Effects on Monosaccharide Transport in Nanochannels. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 114, 11117-11126. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp103519d
Ziemys, A., Kojic, M., Milosevic, M., Kojic, N., Hussain, F., Ferrari, M., Grattoni, A. (2011).Hierarchical modeling of diffusive transport through nanochannels by coupling molecular dynamics with finite element method. Journal of Computational Physics, 230, 5722-5731.DOI: 10.1016/j.jcp.2011.03.054

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Derechos de autor 2022 Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales