Resumen
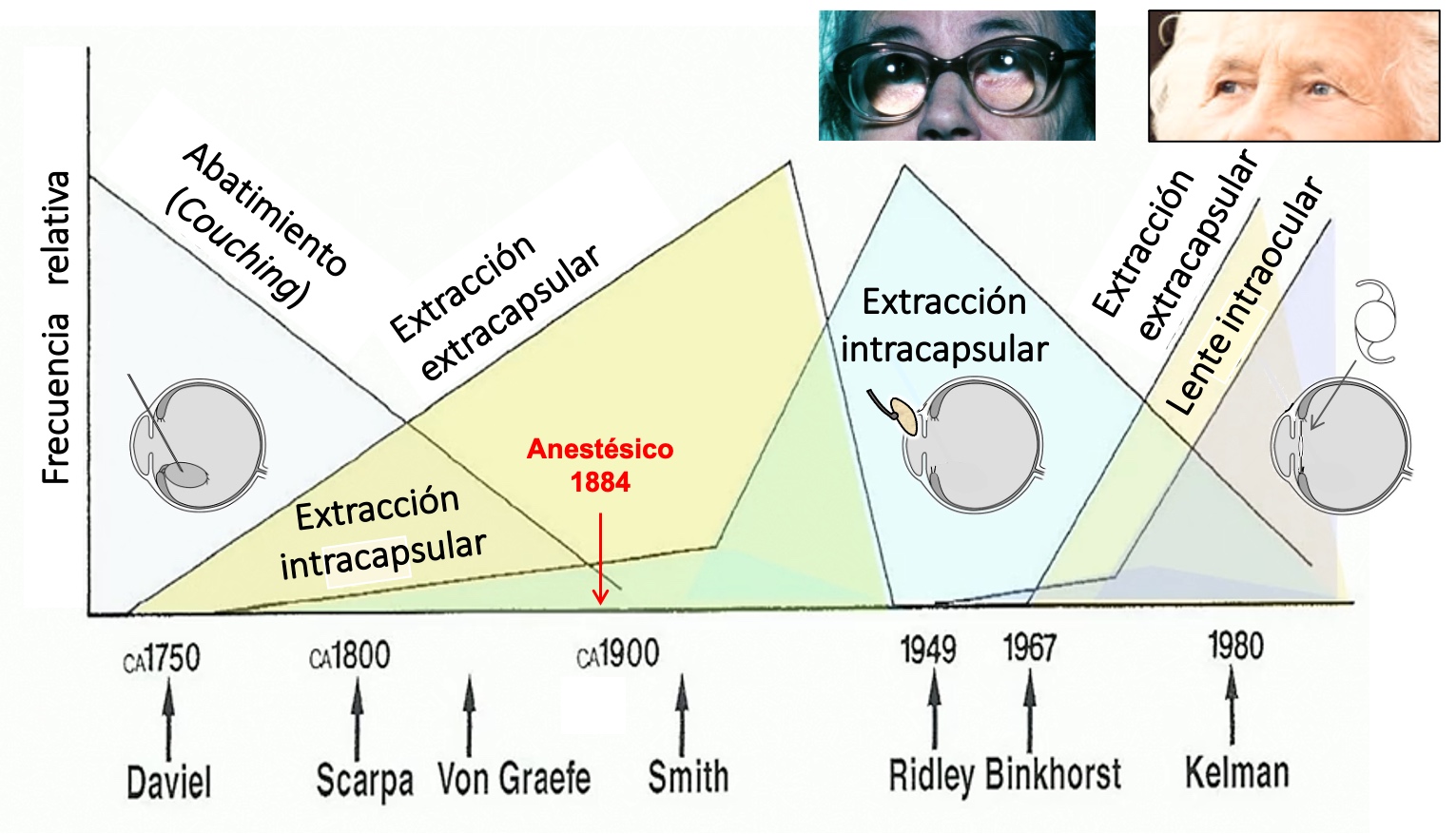
La catarata o pérdida de transparencia del cristalino es un trastorno de la visión muy invalidante que ha sufrido la humanidad a lo largo de la historia. En las últimas décadas se trata con éxito mediante la sustitución de la lente natural por una lente artificial intraocular. Este estudio se centra en los aspectos ópticos, desde el diseño del implante a los efectos en el sistema visual, y en dos temas relacionados con la formación de imágenes de gran interés actualmente: a) los diseños de lentes intraoculares que, además de eliminar la catarata, corrigen parcialmente la presbicia, y b) la calidad de una lente intraocular evaluada por dos vías metodológicas distintas: una óptica (in vitro), en el laboratorio, y otra visual (in vivo) mediante el examen clínico de pacientes con implante. Las métricas que correlacionan ambos métodos buscan una predictibilidad más ajustada de los resultados posoperatorios. Ante la gran variedad de lentes intraoculares existente en la actualidad, on propiedades ópticas notablemente diferentes, se hace necesaria una selección personalizada del implante que mejor se adapte a las características del paciente y tenga en cuenta su estilo de vida.
Palabras clave
Citas
Alarcon, A., Canovas, C., Rosen, R., Weeber, H., Tsai, L., Hileman, K., Piers, P. (2016).Preclinical metrics to predict through-focus visual acuity for pseudophakic patients. BiomedOpt Express. 7 (5): 1877-1888.
Alba-Bueno, F., Vega, F. Millan, M.S. (2011). Design of a Test Bench for Intraocular Lens Optical Characterization. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 274: 012105.
Alba-Bueno, F., Vega, F., Millán, M.S. (2014). Halos and multifocal intraocular lenses: Origin and interpretation. Arch Soc Española Oftalmología (English).89: 397.
Alba-Bueno, F., Garzón, N., Vega, F., Poyales, F., Millán, M.S. (2018). Patient-Perceived and Laboratory-Measured Halos Associated with Diffractive Bifocal and Trifocal IntraocularLenses. Curr Eye Res. 43 (1): 35-42.
Alió, J.L., Alió del Barrio, J.L., Vega-Estrada, A. (2017). Accommodative intraocular lenses: where are we and where we are going. Eye and Vision. 4: 16.
Altmann, G.E. (2005). Aspheric lenses and lens family. U.S. Patent US2005/0203619 A1.
Álvarez, L.W. (1967). Two-element variable-power spherical lens. U.S. patent 3,305,294 (February 21, 1967).
American National Standards Institute, ANSI Z80.35-2018. (2019). Extended depth of focus intraocular lenses. Alexandria, VA U.S.A.: The Vision Council.
Ares, J., Arines, J., Bara, S., Jaroszewicz, Z. (2005). Presbyopia compensation with a quartic lens axicon. Optom. Vis. Sci. 82 (12): 1071-1078.
Armengol, J., Garzón N, Vega F, Altemir I, M.S. Millán. (2020). Equivalence of two optical quality metrics to predict the visual acuity of multifocal pseudophakic patients. Biomed Opt Express. 11 (5): 2818-2829.
Artal, P., Benito, A., Tabernero, J. (2006). The human eye is an example of robust optical design.J Vis. 6: 1-7.
Artal, P., Manzanera, S., Piers, P., Weeber, H. (2010). Visual effect of the combined correction of spherical and longitudinal chromatic aberrations. Opt Express. 18 (2): 1637-1648.
Artal, P. (2014). Optics of the eye and its impact in vision: a tutorial. Adv Opt Photonics. 6 (3): 340-367.
Ascaso, F.J. & Huerva, V. (February 7th, 2013). The History of Cataract Surgery, Cataract Surgery, Farhan Husain Zaidi, IntechOpen. https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/42710. Doi: 10.5772/19243
Atchison, D. A. & Smith, G. (2000). Optics of the human eye. Oxford, United Kingdom: Butterworth-Heinemann. ¿p?
Barbero, S. (2021). Smooth multifocal wavefronts with prescribed mean curvature for visual optics applications. Applied Optics. 60 (21): 6147-6154.
Bernard, Y., Lopez-Gil, N., Legras, R. (2010). Subjective depth of field in presence of 4th-order and 6th-order Zernike spherical aberration using adaptive optics technology. J Cataract. Refract. Surg. 36: 2129-2138.
Breyer, D., Kaymak, H., Ax, T., Kretz, F., Auffarth, G., Hagen, Ph. (2017). Multifocal intraocular lenses and extended depth of focus intraocular lenses. Asia-Pac J Ophthalmol. 6 (4): 339-349.
Campbell, F. W. & Green, D. G. (1965). Optical and retinal factors affecting visual resolution. J Physiol. 181 (3): 576-593.
Cardona, G., Vega, F., Gil, M.A., Varón, C., Buil, J.A., Millán, M.S. (2018). Visual acuity and image quality in 5 diffractive intraocular lenses. Eur J Ophthalmol. 28 (1): 36-41.
Castignoles, F., Flury, M., Lepine, T. (2010). Comparison of the efficiency, MTF and chromatic properties of four diffractive bifocal intraocular lens designs. Opt Express. 18: 5245-5256.
Charman, W. N. (2014). Developments in the correction of presbyopia II: surgical approaches. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 34: 397-426.
Cheng, J.-W., Wei, R.-L., Cai, J.-P., Xi, G.-L., Zhu, H., Li, Y., Ma, X.-Y. (2007). Efficacy of different intraocular lens materials and optic edge designs in preventing posterior capsular opacification: a metanalysis. Am J Ophthalmol. 143: 428-436.
Cohen, A.L. (1993). Diffractive Bifocal Lens Designs. Optom Vis Sci. 70 (6): 461-468.
Davis, G. (2016). The evolution of cataract surgery. Mo Med. 113 (1): 58-62.
Davison, J.A. & Simpson, M.J. (2006). History and development of the apodized diffractive intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 32: 849-858.
Duane, A. (1912). Normal values of the accommodation at all ages, J. Am. Med. Assoc. 59 (12): 1010-1013.
Felipe, A., Pastor, F., Artigas, J. M., Diez-Ajenjo, A., Gené, A., Menezo, J. L. (2010). Correlation between optics quality of multifocal intraocular lenses and visual acuity. Tolerance to modulation transfer function decay. J Cataract Refr Surg. 36 (4): 557-562.
Fernández, D., Barbero, S., Dorronsoro, C., Marcos, S. (2013). Multifocal intraocular lens providing optimized through-focus performance. Opt. Lett. 38 (24): 5303-5306.
Fyodorov, S.N. & Kolonko, A.I. (1967). Estimation of optical power of the intraocular lens (Russian). Vestnik Oftalmologic (Moscow). 4: 27-31.
Gatinel, D., Pagnoulle, Ch., Houbrechts, Y., Gobin, L. (2011). Design and qualification of a diffractive trifocal optical profile for intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refr Surg. 37: 2060-2067.
Goel, S., Chua, C., Butcher, M., Jones, C.A., Bagga, P., Kotta, S. (2004) Laser vs ultrasound biometry—a study of intra-and interobserver variability. Eye. 18: 514-518.
Goodman J. Introduction to Fourier Optics. 4th ed., United States: WH Freeman, 2017. ¿p?
Guirao, A., Redondo, M., Geraghty, E., Piers, P., Norrby, S., Artal, P. (2002). Corneal optical aberrations and retinal image quality in patients in whom monofocal intraocular lenses were implanted. Arch Ophthalmol. 120: 1143-1151.
Gullstrand A. (1909). Apendix II: Procedure of rays in the eye. Imagery -laws of the first order. En Helmholtz’s Handbuch der Physiologischen Optik, vol.1, 3a ed. (traducción inglesa editada por J.P. Southall, Optical Society of America, 1924). ¿p?
Hoffer, K.J., Aramberri, J., Haigis, W., Olsen, Th., Savini, G., Shammas, H.J., Bentow, S. (2015). Protocols for studies of intraocular lens formula accuracy. Am J Ophthalmol. 160 (3): 403-405.
Hoffer K.J. & Savini G. (2020). Update on intraocular lens power calculation study protocols. Ophthalmology; Jul 9; S0161-6420 (30638-2) (Online Epub ahead of print). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2020.07.005
International Organization for Standardization. (2014). ISO 11979-2:2014. Ophthalmic Implants - Intraocular Lenses -Part 2: Optical Properties and Test Methods. Geneva; ISO.
Kolodziejczyk, A., Bara, S., Jaroszewicz, Z., Sypek, M. (1990). The light sword optical element-a new diffractive structure with extended depth of focus. J. Mod. Opt. 37: 1283-1286.
Leffler, C.T., Klebanov, A., Samara, W.A., Grzybowski, A. (2020). “The history of cataract surgery: from couching to phacoemulsification”, Annals of Translational Medicine. 8 (22): 1551.
Marsack, J. D., Thibos, L. N., Applegate, R. A. (2004). Metrics of optical quality derived from wave aberrations predict visual performance. J Vis. 4: 322-328,
Masket, S., Rorer, E., Stark, W., Holladay, J.T., MacRae, S., Eydelman, M. (2017). Special Report: American Academy of Ophthalmology Task Force Consensus Statement for Extended Depth of Focus Intraocular Lenses. Ophthalmology. 124 (1): 139-141.
Melles, R.B., Holladay, J.T., Chang, W.J. (2018). Accuracy of intraocular lens calculation formulas. Ophthalmology. 125: 169-170.
Millán, M.S., Vega, F., Ríos-López, I. (2016). Polychromatic image performance of diffractive bifocal intraocular lenses: Longitudinal chromatic aberration and energy efficiency. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 57 (4): 2021-2028.
Millán M.S., Vega, F. (2017). Extended depth of focus intraocular lens: chromatic performance.Biomed Opt Express. 8 (9): 4294-4309.
Millán M.S., Pérez, E., Vega, F. (2017). System and method for characterizing, designing and/or modifying optical properties of a lens. Patent No. PCT/IB2017/000044.
Montés-Micó, R., Ferrer-Blasco, T., Cerviño, A. (2009). Analysis of the possible benefits of aspheric intraocular lenses: review of the literature. Journal of Cataract and Refractive Surgery. 35: 172-181.
Navarro, R. (2009). The optical design of the human eye: a critical review. Journal of Optometry.2 (1): 3-18.
Navarro, R. (2009). Letter to the editor. Journal of Optometry. 2: 163-164.
Norrby, S., Piers, P., Campbell, Ch., van der Mooren, M. (2007). Model eyes for evaluation of intraocular lenses,” Applied Optics. 46 (26): 6595-6605.
Ojeda-Castañeda, J. & Gómez-Sarabia, C. (2015). Tuning field depth at high resolution by pupil engineering. Advances in Optics and Photonics. 7: 814-880.
Petelczyc, K., Byszewska, A., Chojnacka, E., Jaroszewicz, Z., Kakarenko, K., Mira-Agudelo, A., Ostrowska-Spaleniak, A., Składowska, A., Kołodziejczyk, A., Rekas, M. (2019). The Light Sword Lens - A novel method of presbyopia compensation: Pilot clinical study. PLoS ONE. 142: e0211823.
Piers, P.A., Weeber, H.A., Artal, P., Norrby S. (2007). Theoretical comparison of aberration-correcting customized and aspheric intraocular lenses. Journal of Refractive Surgery. 23:374-384.
Ravikumar, S., Bradley, A., Thibos, L.N. (2014). Chromatic aberration and polychromatic image quality with diffractive multifocal intraocular lenses. Journal of Cataract and Refractive Surgery. 40: 1192-1204.
Remón, L., García-Delpech, S., Udaondo, P., Ferrando, V., Monsoriu, J.A., Furlan, W.D. (2018).Fractal-structured multifocal intraocular lens. PLoS ONE. 13 (7): e0200197.
Romero, L.A., Millán, M.S., Jaroszewicz, Z., Kolodziejczyk, A. (2012). Double peacock eye optical element for extended focal depth imaging with ophthalmic applications. J. Biomed. Opt. 17 (4): 046013.
Schwartz, D.M., Sandstedt, C.A., Chang, S.H., Kornfield, J.A., Grubbs, R.H. (2004). Light-adjustable lens: development of in vitro nomograms. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 102: 67-74.
Schwiergerling, J. & Greivenkamp, J.E. (1997). Using corneal height maps and polynomial decomposition to determine corneal aberration. Optom Vis Sci. 74: 906-916.
Simonov, A. N., Vdovin, G., Rombach, M. C. (2006). Cubic optical elements for an accommodativeintraocular lens. Optics Express. 14 (17): 7757-7775
Spalton, D. (2019). The origins of cataract surgery. Heritage Lecture ESCRS Congress, París (16th Sep 2019).https://player.escrs.org/featured/escrsheritage-lecture-2019-the-origins-of-cataract-surgery-david-spalton
Thibos, L.N., Ye, M., Zhang, X., Bradley, A. (1992). The chromatic eye: a new reduced-eye model of ocular chromatic aberration in humans. Appl. Opt. 31 (19): 3594-3600.
Thibos, L.N., Hong, X., Bradley, A., Applegate, R.A. (2004). Accuracy and precision of objective refraction from wavefront aberrations. J Vis. 4: 329-351.
Van der Mooren, M., Franssen, L., Piers, P. (2013). Effects of glistenings in intraocular lenses.Biomed Opt Express. 4 (8): 1294-1304.
Vega, F., Alba-Bueno, F., Millán, M.S. (2011). Energy distribution between distance and near images in apodized diffractive multifocal intraocular lenses. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci.52 (8): 5695-5701.
Vega, F., Millán, M.S., Garzón, N., Altemir, I., Poyales, F., Larrosa, J. M. (2018). Visual acuity of pseudophakic patients predicted from in-vitro measurements of intraocular lenses with different design. Biomed Opt Express. 9 (10): 4893-4906.
Vega, F., Valentino, M., Rigato, F., Millán, M.S. (2021). Optical design and performance of a trifocal sinusoidal diffractive intraocular lens. Biomed Opt Express. 12 (6): 3338-3351.
Villegas, E.A., Alcón, E., Mirabet, S., Yago, I., Marín, J.M., Artal, P. (2014). Extended depth of focus with induced spherical aberration in light adjustable intraocular lenses. American Journal of Ophthalmology. 157 (1): 142-149.
Vinas, M., Benedi-García, C., Aissati, S., Pascual, D., Akondi, V., Dorronsoro, C., Marcos, S.(2019). Visual simulators replicate vision with multifocal lenses. Sci Rep. 9: 1539.
Wang, W., Yan, W., Fotis, K., Prasad, N.M., Lansingh, V.Ch., Taylor, H.R. Finger, R.P., Facciolom D., He, M. (2016). Cataract surgical rate and socioeconomics: a global study.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 57: 5872-5881.
Weeber, H.A. & Piers, P.A. (2012). Theoretical performance of intraocular lenses correcting both spherical and chromatic aberration. J Refract Surg. 28 (1): 48-52.
Yang, H. & Afshari NA. (2014). The yellow intraocular lens and the natural ageing lens. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 25 (1): 40-3.
Yeu E. & Cuozzo S. (2020) Matching the Patient to the Intraocular Lens: Preoperative Considerations to Optimize Surgical Outcomes. Ophthalmology. 2020 Aug 31:S0161-6420(20)30843-5.
Zalevsky, Z., Shemer, A., Zlotnik, A., Eliezer, E.B., Marom, E. (2006). All-optical axial super resolving imaging using a low-frequency binary-phase mask. Optics Express. 14: 2631-2643.
Zeng, L. & Fang, F. (2018). Advances and challenges of intraocular lens design. Appl Opt. 57 (25):7363-7376.
Zhou, F., Ye, R., Li, G., Zhang, H., Wang, D. (2009). Optimized circularly symmetric phase mask to extend the depth of focus. Journal of the Optical Society of America. 26: 1889-1895.

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Derechos de autor 2021 Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales