Resumen
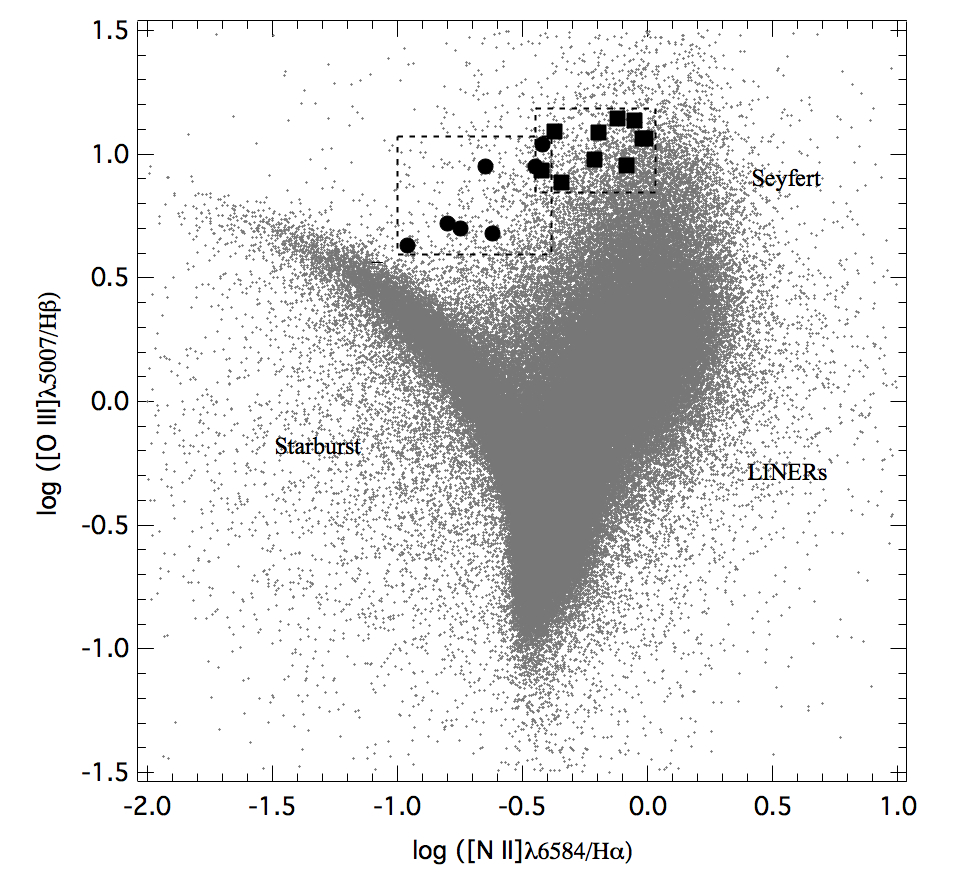
En estudios recientes se ha evidenciado que la región de emisión de líneas coronales observada en algunos núcleos galácticos activos está localizada en la cara interna del toroide oscurecedor; sin embargo, hay numerosos ejemplos de galaxias Seyfert 2 con significativa emisión coronal. Para aclarar esta anomalía, en el presente trabajo nos propusimos ofrecer algunas ideas sobre la ubicación espacial de la región de líneas coronales (RLC) en galaxias de tipo Seyfert 2, así como determinar las condiciones físicas del gas coronal para este tipo de galaxias. Para ello se ejecutó una rutina en SQL en la base de datos del Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS-DR14) con el propósito de seleccionar varias galaxias de tipo Seyfert 2 bajo los siguientes criterios: 3<[O III] λ5007/ Hβ<16, 0.5 <[N II] λ6584/Hα<2, 0.3<([S II] λ6717+λ6731)/Hα<0.6, 0.06<[O I] λ6300/Hα<0.2 y 0.02 < z < 0.13. El procedimiento arrojó 497 galaxias Seyfert 2. De esta muestra, se detectó emisión simultánea en las cuatro líneas prohibidas de alta ionización del [Fe VII] λλλλ6087, 5721, 5158, 3759 en 10 objetos. A partir de las relaciones de flujo de esas cuatro líneas se establecieron los rangos de densidad y temperatura electrónica de la región de emisión por dos vías, lo que permitió un acotamiento más aproximado de tales valores. Al compararlos con los obtenidos para la región de líneas delgadas (RLD), se encontró una correlación entre las temperaturas de la RLC y la RLD, lo que sugiere algún tipo de conexión física entre ambas zonas de este tipo de objetos.
Referencias
Abolfathi, B., et al. (2018). The fourteenth data release of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey: First spectroscopic data from the Extended Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey and from the second phase of the Apache Point Observatory Galactic Evolution Experiment. The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 235: 1-19. Doi: 10.3847/1538-4365/aa9e8a
Antonucci, R. (1993). Unified models for active galactic nuclei and quasars. Annual review of astronomy and astrophysics. 31: 473-521. Doi: 10.1146/annurev.aa.31.090193.002353
Baldwin, J. A., Phillips, M. M., Terlevich, R. (1981). Classification parameters for the emissionline spectra of extragalactic objects. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 93: 5-19. Doi: 10.1086/130766
Berrington, K. A., Nakazaki, S., & Norrington, P. H. (2000). Atomic data from the IRON Project-XLI. Electron excitation rates among the 3d2 fine-structure levels of Ca-like Fe VII. Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series. 142: 313-316. Doi: 10.1051/aas:2000152
Cardona, G. & Portilla, J. G. (2015). Líneas prohibidas de alta ionización en una muestra de cuásares. Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales. 152:321-327. Doi: 10.18257/raccefyn.224
Colina, L., Sparks, W. B., Macchetto, F. (1991). IC 5063: A merger remnant with a hidden luminous active nucleus. The Astrophysical Journal. 370: 102-117. Doi: 10.1086/169795 Crenshaw, D. M., Peterson, B. M., Korista, K. T., Wagner, R. M., Aufdenberg, J. P. (1991).
Ultraviolet and Optical Spectra of High-ionization Seyfert galaxies with Narrow Lines. The Astrophysical Journal. 101: 1202-1206. Doi: 10.1086/115757
De Robertis, M. M., Dufour, R. J., Hunt, R. W. (1987). A five-level program for ions of astrophysical interest. Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada. 81: 195-220.
Dere, K. P., Landi, E., Mason, H. E., Masignori Fossi, B. C., Young, P. R. (1997). CHIANTIan atomic database for emission lines-I. Wavelengths greater than 50 Å, Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series. 125: 149-173. Doi: 10.1051/AAS:1997368
Emerson, D. (1996). Interpreting astronomical spectra, Jhon Wiley & Sons, London. p 207.
Ferguson, J. W., Korista, K. T., Ferland, G. J. (1997). Physical conditions of the coronal line region in Seyfert galaxies, The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 110: 287-297. Doi: 10.1086/312998
Gelbord J. Mullaney, J. R., Ward, M. J. (2009). AGN with strong forbidden high-ionization lines selected from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 397: 172-189. Doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.14961.x
Glidden, A., Rose, M., Elvis, M., McDowell, J. (2016). A model for type 2 coronal line forest (CLiF) AGNs. The Astrophysical Journal. 824: 34-41. Doi: 10.3847/0004-637X/824/1/34
González R. M. & Pérez, E. (1996) A spectrophotometric study of the Seyfert 1 Galaxy NGC 4253. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 278: 737-748. Doi: 10.1093/mnras/278.3.737
Khachikian, E. D. & Weedman, D. W. (1974). An atlas of Seyfert galaxies. The Astrophysical Journal. 192: 581-589. Doi: 10.1086/153093
Keenan, F. P. & Norrington, P. H. (1987). Relative emission line strengths for Fe VII in astrophysical plasmas. Astronomy & Astrophysics. 181: 370-372.
Keenan, F. P. & Norrington, P. H. (1991). Relative populations for levels in the 3d2 ground configuration of Fe VII. The Astrophysical Journal. 368: 486-490. Doi: 10.1086/169713
Keenan, F. P., Aller, L. H., Ryans, R. S. I., Hyung, S. (2001). Theoretical emission line ratios for [Fe III] and [Fe VII] applicable to the optical and infrared spectra of gaseous nebulae. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 98: 9476-9477. Doi: 10.1073/pnas.151263098
Komossa, S., Zhou, H., Rau, A., Dopita, M., Gal-Yam, A., Greiner, J., Zuther, J., Salvato, M., Xu, D., Lu, H., Saxton R., Ajello, M. (2009). NTT, Spitzer and Chandra spectroscopy of SDSSJ095209. 56+214313.3: the most luminous coronal-line supernova ever observed, or a stellar tidal disruption event? The Astrophysical Journal. 701: 105-121. Doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/701/1/105
Korista, K. & Ferland, G. J. (1989). The origin of coronal lines in Seyfert galaxies. The Astrophysical Journal. 343: 678-685. Doi: 10.1086/167739
Koski, A. T. (1978). Spectrophotometry of Seyfert 2 galaxies and narrow-line radio galaxies. The Astrophysical Journal. 223: 56-73. Doi: 10.1086/156235
Mazzalay, X., Rodríguez-Ardila, A., Komossa, S. (2010). Demystifying the coronal-line region of active galactic nuclei: spatially resolved spectroscopy with the Hubble Space Telescope.
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 405: 1315-1338. Doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16533.x
Murayama, T. & Taniguchi, Y. (1998a). Where is the coronal line region in active galactic nuclei? The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 497: L9-L12. Doi: 10.1086/311264
Murayama, T. & Taniguchi, Y. (1998b). A New Dual-Component Photoionization Model for the Narrow Emission Line Regions in Active Galactic Nuclei. The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 503: L115-L118. Doi: 10.1086/311554
Nussbaumer H. & Storey, P. J. (1982). Forbidden emission lines of Fe VII. Astronomy & Astrophysics. 113: 21-26.
Oke, J. B. & Sargent, W. L. W. (1968). The nucleus of the Seyfert Galaxy NGC 4151. The Astrophysical Journal. 151: 807-823.
Osterbrock, D. E. (1969). Calculated [Fe X] and [Fe XIV] Line Strengths in a Seyfert Galaxy Model. Astrophysical Letters. 4: 57-59.
Osterbrock, D. E. (1993). The nature and structure of active galactic nuclei. The Astrophysical Journal. 404: 551-562. Doi: 10.1086/172307
Osterbrock, D. E. & Ferland, G. J. (2006). Astrophysics of gaseous nebulae and active galactic nuclei. University Science Books. Sausalito. p. 329.
Penston, M. V., Fosbury, R. A. E., Boksenberg, A., Waed, M. J., Wilson, A. S. (1984). The Fe(9+) region in active galactic nuclei. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 208: 347-364. Doi: 10.1093/mnras/208.2.347
Peterson, B. M. (1997). An introduction to active galactic nuclei, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. p. 21.
Pier, E. A. & Voit, G. M. (1995). Photoevaporation of dusty clouds near active galactic nuclei. The Astrophysical Journal. 450: 628-637. Doi: 10.1086/176171
Portilla, J. G. (2012). La región de líneas coronales en galaxias Seyfert 1 y Seyfert 2, (Doctoral dissertation, Universidad Nacional de Colombia).
Rodríguez-Ardila, A. & Fonseca-Faria, M. (2020). A 700 pc extended coronal gas emission in the Circinus galaxy. The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 895: 1-5. Doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/ab901b
Rose, M., Elvis, M., Tadhunter, C. N. (2015). Coronal-line forest AGN: the best view of the inner edge of the AGN torus? Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 448: 2900-2920. Doi: 10.1093/mnras/stv113
Rose, M., Elvis, M., Crenshaw, M., Glidden, A. (2015). Intermediate inclinations of type 2 coronalline forest AGN. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 451: L11-L15. Doi: 10.1093/mnrasl/slv056
Vaona, L., Ciroi, S., Di Mille, F., Cracco, V., La Mura, G., Rafanelli, P. (2012). Spectral properties of the narrow-line region in Seyfert galaxies selected from the SDSS-DR7. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 427: 1266-1283. Doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.22060.x
Veron-Cetty, M. P., Joly, M., Veron, P. (2004). The unusual emission line spectrum of I Zw 1. Astronomy & Astrophysics. 417: 515-525. Doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20035714
Veron-Cetty, M. P. & Veron, P. (2006). A catalogue of quasars and active nuclei. Astronomy & Astrophysics. 455: 773-777. Doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20065177
Viegas-Aldrovandi, S. M. & Contini, M. (1989). Composite models for the narrow emission-line region of active galactic nuclei. VI-The Fe lines. Astronomy & Astrophysics. 215: 253-261.
Wang, T-G., Zhou, H-Y., Komossa, S., Wang, H-Y., Yuan, W., Yang, C. (2012). Extreme coronal line emitters: Tidal disruption of stars by massive black holes in galactic nuclei? The Astrophysical Journal. 749 (2): 115-130. Doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/749/2/115

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Derechos de autor 2021 Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales