Resumen
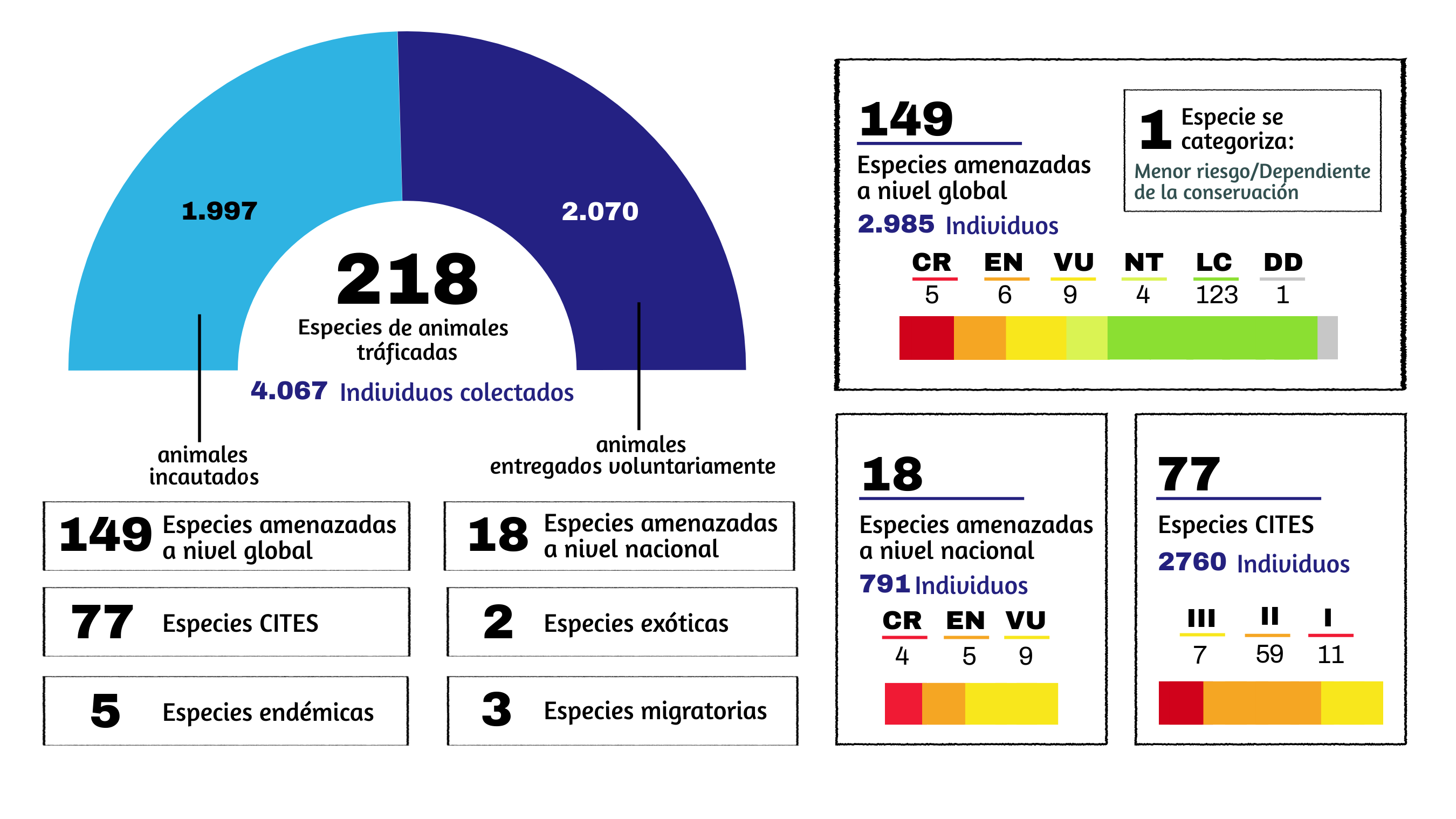
El tráfico ilegal de especies es una actividad delictiva muy lucrativa que amenaza la supervivencia de numerosas especies. El departamento del Tolima, centro de Colombia, es considerado un hotspot para estas actividades debido a su rica biodiversidad y ubicación estratégica. Con el propósito de conocer el comportamiento del tráfico ilegal de fauna silvestre en este departamento, se analizó el número de reportes de incautación y entregas voluntarias entre el 2013 y el 2022 a partir de la información proporcionada por la Corporación Autónoma Regional del Tolima (Cortolima). Se registraron 4.067 individuos pertenecientes a 218 especies, 150 géneros, 96 familias y 45 órdenes. Las aves fueron el grupo más traficado (56,2 %), seguido de los reptiles (34,25 %) y los mamíferos (6,68 %). Entre las especies más afectadas se encuentran la tortuga morrocoy (Chelonoidis carbonarius), el loro común (Amazona ochrocephala) y el periquito bronceado (Brotogeris jugularis). El 9,17 % de las especies registradas están amenazadas a nivel internacional y el 8,25 % a nivel nacional, en tanto que el 35,32 % se encuentra en los apéndices de la Convención sobre el Comercio Internacional de Especies Amenazadas de Fauna y Flora Silvestres - CITES. Los años 2021 (21,63 %) y 2016 (18,28 %) fueron los del mayor número de incautaciones, mientras que el 2013 (33,91 %), el 2014 (29,32 %) y el 2015 (24,54 %) registraron el mayor número de entregas voluntarias de especies a Cortolima. La zona central del departamento fue la más representativa a lo largo del periodo estudiado (66,24 %). Estos hallazgos brindan una visión detallada y actualizada del tráfico ilegal de especies en el Tolima, lo que es esencial para diseñar e implementar medidas de conservación y protección de especies amenazadas.
Referencias
Arbeláez-Cortés, E. (2013). Knowledge of Colombian biodiversity: published and indexed. Biodiversity and conservation, 22, 2875-2906.
Arroyave-Bermúdez, F. J., Romero-Goyeneche, O. Y., Bonilla-Gómez, M. A., Hurtado-Heredia, R.G. (fecha). Tráfico ilegal de tortugas continentales (Testudinata) en Colombia: una aproximación desde el análisis de redes. Acta Biológica Colombiana, 19(3), 381-392.
Arroyave-Bermúdez, F. (2015). El tráfico ilegal de reptiles en Colombia: una aplicación del análisis de redes a las relaciones ambientales. Trabajo de grado. Universidad Nacional de Colombia.
Baptiste M.P., Vargas-Tovar, N., Osorno, M., Cárdenas-López, D., González, M. (2014). Tráfico ilegal de especies. En: Bello et al. (Eds.). Biodiversidad 2014. Estado y tendencias de la biodiversidad continental en Colombia. Instituto Alexander von Humboldt.
Bello, A. C. (2010). Tráfico y tenencia ilegal de fauna silvestre en el departamento de Boyacá. Cultura Científica, Volumen (8), 16-23.
Bonilla, M. A., Luque, N., Cuervo, M. A., Pinzón, M., Vásquez, E. A. (2014). Ecología de tortugas terrestres y de agua dulce de colombia y manejo de decomisos. Editorial Universidad Nacional de Colombia.
Cáceres-Martínez, C. H., Villamizar, M. P., Arias-Alzate, A. (2017). Diagnóstico sobre el tráfico de fauna silvestre en el departamento de Norte de Santander, Colombia. Revista Biodiversidad Neotropical, 7(3), 189-199.
Castro-Cortés, A. A., Brieva, C., Witte, C. (2022). Implications of wildlife trafficking on the health and conservation efforts of an endangered turtle species in Colombia. Conservation Science and Practice, 4(3), e595.
Chamat, A. G. (2022). Tráfico ilegal de aves silvestres: Propuesta de nuevas acciones para Colombia a partir de la revisión de experiencias internacionales. Tesis de maestría. Pontificia Universidad Javeriana.
Contraloría General de la República. (2014). Análisis de la política de gestión ambiental de fauna silvestre y de la estrategia para la prevención y el control del tráfico ilegal de especies silvestres 2008-2013, pp. 304-407. Contraloría General de la República.
Correa-Ayram, C. A., Etter, A., Díaz-Timoté, J., Rodríguez-Buriticá, S., Ramírez, W., Corzo, G. (2020). Spatiotemporal evaluation of the human footprint in Colombia: Four decades of anthropic impact in highly biodiverse ecosystems. Ecological Indicators, 117, 106630.
Corporación Autónoma Regional del Tolima (CORTOLIMA) (2009). Plan de acción trienal 2007-2009. Corporación Autónoma del Tolima.
Crespo, S., Solórzano, C., Guerrero, J. (2022). Tráfico nacional de fauna silvestre y especies amenazadas: un estudio descriptivo en Manabí (Ecuador). Revista de Ciencias de la Vida, 35(1), 33-44.
Cruz, D. & Gómez, J. R. (2011). Aproximación al uso y tráfico de fauna silvestre en Puerto Carreño, Vichada. Colombia Ambiente y Desarrollo, 14(26), 63.
Cruz-Rodríguez, C. A., Pérez-Torres, J., González-Maya, J. F. (2017). Resolución nacional de especies amenazadas de Colombia. Mammalogy Notes, 4(2), 1-5.
Doherty, T. S., Glen, A. S., Nimmo, D. G., Ritchie, E. G., Dickman, C. R. (2016). Invasive predators and global biodiversity loss. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113 (40), 11261-11265. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1602480113
Duffy, R., St John, F. A., Büscher, B., Brockington, D. (2016). Toward a new understanding of the links between poverty and illegal wildlife hunting. Conservation Biology, 30(1), 14-22.
Etter, A., McAlpine, C., Wilson, K., Phinn, S., Possingham, H. (2006). Regional patterns of agricultural land use and deforestation in Colombia. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 114(2-4), 369-386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2005.11.013
Esmail, N., Wintle, B. C., t Sas-Rolfes, M., Athanas, A., Beale, C. M., Bending, Z., Dai, R., Fabinyi, M., Gluszek, S., Haenlein, C., Harrington, L. A., Hinsley, A., Kariuki, K., Lam, J., Markus, M., Paudel, K., Shukhova, S., Sutherland, W. J., Verissimo, D., Wang, Y., Waugh, J., Wetton, J. H., Workman, C., Wright, J., Milner-Gulland, E. J. (2020). Emerging illegal wildlife trade issues: A global horizon scan. Conservation Letters, 13(4), [e12715]. https://doi.org/10.1111/conl.12715
Gluszek, S., Ariano-Sánchez, D., Cremona, P.J., Goyenechea, A., Luque-Vergara, D.A., Mcloughlin, L., Morales, A., Reuter-Cortés, A., Rodríguez-Fonseca, J., Radachowsky, J., Knight, A.T. (2020). Emerging trends of the illegal wildlife trade in Mesoamerica. Oryx, 55, 708 - 716.
González-Maya, J.F., Lemus-Mejía, L., Morales-Perdomo, J., Moreno-Díaz, C., Zárrate-Charry, D.A. (Eds.) (2022). Mamíferos de Cundinamarca: diversidad, conservación y cambio climático. Corporación Universitaria Minuto de Dios.
Hughes, A. C. (2021). Wildlife trade. Current Biology, 31(19), R1218-R1224.
Hernández, D., Pulido, M., Zuria, I., Gallina, S., Sánchez, G. (2018). El manejo como herramienta para la conservación y aprovechamiento de la fauna silvestre: acceso a la sustentabilidad en México. Acta Universitaria, 28 (4), 31-41. https://doi.org/10.15174/au.2018.2171
Hughes, L. J., Morton, O., Scheffers, B. R., Edwards, D. P. (2023). The ecological drivers and consequences of wildlife trade. Biological Reviews, 98(3), 775-791. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12929
Izquierdo-Páez, J. P. (2021). Caracterización de la dinámica del tráfico ilegal de fauna silvestre en Colombia y en el Distrito Capital entre los años 2005 y 2019. Tesis de maestría. Pontificia Universidad Javeriana. http://hdl.handle.net/10554/59462
Kassambara, A. & Kassambara, M. A. (2020). Package ‘ggpubr’. R package version 0.1, 6 (0).
Mancera-Rodríguez, N. J. & Reyes-García, O. (2008). Comercio de fauna silvestre en Colombia. Revista Facultad Nacional de Agronomía Medellín, 61(2), 4618-4645.
Márquez, G., Bojórquez, A., Hernández, G. (2020). El tráfico ilegal de especies silvestres. Una pérdida del patrimonio natural. Grupo eumed, XIV Congreso Virtual Internacional Turismo y Desarrollo.
Mellor, D., Patterson-Kane, E., Stafford, K. J. (2009). The sciences of animal welfare. John Wiley & Sons.
Ministerio de Ambiente y Desarrollo Sostenible (2012). Estrategia Nacional para la prevención y control al Tráfico Ilegal de Especies Silvestres: Diagnóstico y Plan de Acción ajustado; Colombia. Ministerio de Ambiente y Desarrollo Sostenible.
Morales-David, C. & Mancera-Rodríguez, N. J. (2021). Manejo, valoración y atención de la fauna silvestre en el departamento del Valle del Cauca, Colombia. Revista Luna Azul, Volumen (52), 105-125.
Mosquera, F., Trujillo, F., Aya, C., Bolívar, L., Valencia, K., Arboleda, A.F., Mantilla, H. (2019). Mamíferos. En: F. Trujillo & F. Anzola (eds). Biodiversidad en el departamento de Arauca. Gobernación de Arauca, Fundación Omacha y Fundación Ecollano.
Myers, N., Mittermeier, R. A., Mittermeier, C. G., Da Fonseca, G. A., Kent, J. (2000). Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature, 403(6772), 853-858.
Nellemann, C., Henriksen, R., Kreilhuber, A., Stewart, D., Kotsovou, M., Raxter, P., Mrema, E., Barrat, S. (2016). The rise of environmental crime: a growing threat to natural resources, peace, development and security. United Nations Environment Programme.
Ogle, D., Wheeler, P., Dinno, A. (2017). Package ‘FSA’. Cran Repos, 1-206.
Oksanen, J., Simpson, G., Blanchet, F., Kindt, R., Legendre, P., Minchin, P., O’Hara, R., Solymos, P., Stevens, M., Szoecs, E., Wagner, H., Barbour, M., Bedward, M., Bolker, B., Borcard, D., Carvalho, G., Chirico, M., De Caceres, M., Durand, S., … Weedon, J. (2022). Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.6-4. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan
Ortiz-Calderón, M. I. & Acero-Plazas, V. M. (2022). Riesgos del tráfico ilegal de aves silvestres en Bogotá (Colombia) según la perspectiva Una Salud. Boletín Epidemiológico Distrital - Bed, 19(8-12), 71-72. https://doi.org/10.56085/01238590.526
Pedersen, T. (2022). Patchwork: The Composer of Plots. R package version 1.1.2, https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=patchwork
Phelps, J., Biggs, D., Webb, E. L. (2016). Tools and terms for understanding illegal wildlife trade. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 14(9), 479-489.
Pino-Varón, J. A., & Piedrahita-Hincapié, L. C. (2023). Tráfico ilegal de especies silvestres en Colombia: problemáticas emergentes y nuevas tendencias. Universidad Libre. https://hdl.handle.net/10901/25724
R Core Team (2021). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/.
Rangel - Ch., J. O. (2015). La biodiversidad de Colombia: significado y distribución regional. Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales, 39(151), 176–200. https://doi.org/10.18257/raccefyn.136
Restrepo-Rodas, D. C. & Pulgarín-Restrepo, P. C. (2021). Dinámicas de los loros en cautiverio en Colombia: tráfico, mortalidad y liberación: Captivity parrots in Colombia: traffic, mortality and liberation. Ornitología Colombiana, Volumen (16), 1-23.
Ribeiro, J., Reino, L., Schindler, S., Strubbe, D., Vall-Llosera, M., Araújo, M.B., Capinha, C., Carrete, M., Mazzoni, S., Monteiro, M., Moreira, F., Rocha, R., Tella, J.L., Vaz, A.S., Vicente, J.R., Nuno, A. (2019). Trends in legal and illegal trade of wild birds: a global assessment based on expert knowledge. Biodiversity and Conservation, 28, 3343 - 3369.
Rodríguez-Chavarro, A. M. (2022). Diseño de un sitio Web para el reconocimiento de psitácidos de Colombia sensibles al tráfico ilegal como propuesta para el desarrollo de actitudes de conservación a partir del análisis ecológico. Trabajo de grado. Universidad Pedagógica Nacional.
Rojas-Briñez, D. K. (2011). Comercio de fauna Silvestre en el departamento del Tolima-Colombia bajo el contexto de la demanda internacional de especies. Tesis de maestría. Universidad Internacional de Andalucía.
Rojas-Briñez, D.K., Regis-Silva, M., García-Melo, J.E. (2013). Estado actual y perspectivas de conservación frente al comercio ilegal de fauna silvestre en el departamento del Tolima (Colombia). Revista Tumbaga, 1 (8), 97-111.
Romero-Cortés, C. A. (2019). El tráfico de especies: un punto ciego de la seguridad en las cadenas de suministro. Tesis, Relaciones Internacionales y Estudios Políticos, Universidad Militar Nueva Granada, Colombia. http://hdl.handle.net/10654/21140
Roncancio, N., Branch, J., Moreno-Mancilla, O. F., Ospina, O., Guzmán, L. M. (2020). Reducción en la densidad poblacional del tití gris (Saguinus leucopus) en el oriente de Caldas, Colombia. Neotropical primates, 26(1), 56-63.
Rosen, G. E. & Smith, K. F. (2010). Summarizing the evidence on the international trade in illegal wildlife. EcoHealth, 7, 24-32.
Rush, E. R., Dale, E., Aguirre, A. A. (2021). Illegal wildlife trade and emerging infectious diseases: pervasive impacts to species, ecosystems and human health. Animals, 11(6), 1821.
Sas-Rolfes, M.t., Challender, D. W., Hinsley, A., Veríssimo, D., Milner-Gulland, E. J. (2019). Illegal wildlife trade: Scale, processes, and governance. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 44, 201-228.
SiB Colombia (2022). Biodiversidad en Cifras, Sistema de Información sobre Biodiversidad de Colombia. https://biodiversidad.co/consultar/biodiversidad-cifras-colombia/
Silva-Arias, A. C. & González-Román, P. (2009). Un análisis espacial de las migraciones internas en Colombia (2000-2005). Revista Facultad de Ciencias Económicas: Investigación y Reflexión, 17(1), 123-144.
Sollund, R. (2017). The use and abuse of animals in wildlife trafficking in Colombia: Practices and injustice. Environmental crime in Latin America: The theft of nature and the poisoning of the land. Springer.
Southwick, N. (2013). 58000 animales confiscados anualmente en Colombia. Centro de Investigación de Crimen Organizado. https://es.insightcrime.org/noticias/noticias-del-dia/58000-animales-traficados-son-confiscados-anualmente-en-colombia/
Sumaila, U. R., Zeller, D., Hood, L., Palomares, M. L. D., Li, Y., Pauly, D. (2020). Illicit trade in marine fish catch and its effects on ecosystems and people worldwide. Science advances, 6 (9), eaaz3801.
Tournant, P., Joseph, L., Goka, K., Courchamp, F. (2012). The rarity and overexploitation paradox: stag beetle collections in Japan. Biodiversity and Conservation, 21, 1425-1440.
UNEP-WCMC (2023). The Checklist of CITES Species Website. CITES Secretariat, Geneva, Switzerland. Compiled by UNEP-WCMC, Cambridge, UK. http://checklist.cites.org
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime-UNODC (2016). World Wildlife Crime Report: Trafficking in Protected species. UNODC, New York, USA.
Valencia-González, C. (2018). Fauna silvestre en Colombia: entre la ilegalidad y las oportunidades del comercio internacional en la CITES. Revista Virtual Universidad Católica del Norte, Volumen (55), 128 - 145.
Van Uhm, D. P. (2016). The illegal wildlife trade: Inside the world of poachers, smugglers and traders (Vol. 15). Springer.
Wickham, H., Chang, W., Henry, l., Takahashi, K., Wilke, C., Woo, K., Yutani, H. Dunnington, D., van den Brand, T. (2016). Package ggplot2. Create elegant data visualisations using the grammar of graphics.
Wickham, H. & Seidel, D. (2022). Scales: Scale Functions for visualization. R package version 1.2.1. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=scales
Wyatt, T., van Uhm, D., Nurse, A. (2020). Differentiating criminal networks in the illegal wildlife trade: organized, corporate and disorganized crime. Trends in Organized Crime, 23, 350–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12117-020-09385-9

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Derechos de autor 2024 Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales