Resumen
El sistema ZnO dopado con Fe presenta buenas propiedades como semiconductor magnético diluido para aplicaciones en espintrónica. En este artículo se hace una revisión de algunas propiedades estructurales y magnéticas del ZnO dopado con Fe. Inicialmente, se hace un resumen de los conceptos básicos para entender en qué consiste la espintrónica y sus posibles aplicaciones. Posteriormente, se presenta el estudio de dicho sistema mediante difracción de rayos X, espectroscopía Mössbauer y magnetometría de muestra vibrante en muestras obtenidas por aleamiento mecánico en diferentes condiciones de preparación. En la primera se aumentó la concentración de Fe de 3 a 10 % en un tiempo de molienda de 36 horas y una relación entre el peso de las bolas y el peso de los elementos (relación de peso bolas-polvo, RPB) de 15:1. En este caso se probó que hubo una concentración límite de Fe, aproximadamente de 5 %, que se diluyó dentro de la red del ZnO; el resto del Fe apareció segregado en la muestra. En la segunda condición se fijó la concentración de Fe en 10 % y se variaron las horas de molienda. Se encontró que después de 24 horas, la muestra se consolidó, pero el Fe no se diluyó completamente dentro de la red de ZnO. Por último, usando una concentración de 10 % en Fe y aumentando la RPB se encontró que todos los átomos de Fe se diluyeron dentro de la fase de ZnO y no quedaron segregados de Fe en la muestra, lo que se explica porque al aumentar la relación RPB aumenta la energía.
Referencias
Ahmed, S.A. (2017). Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Mn-doped ZnO samples. Results Phy. 7: 604. Doi: 10.1016/J.RINP.2017.01.018
Alsaad, A. (2014). Structural, electronic and magnetic properties of Fe, Co, Mn-doped GaN and ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductors Physica B. 440: 1-9. Doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2014.01.029
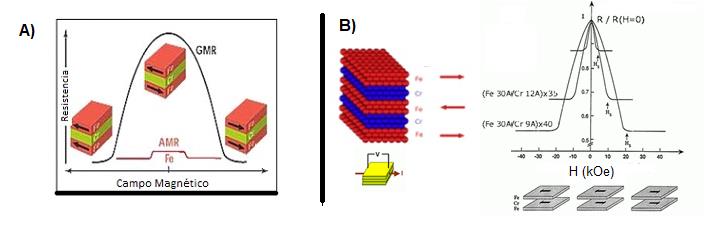
Baibich, G M.N., Broto, J.M., Fert, A., van Dau, F.N., Petroff, F., Etienne, P., Creuzet, G., Friederich, A., Chazelas, J. (1988). Giant Magnetoresistance of (001)Fe/(001)Cr Magnetic Superlattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 61: 2472. Doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.61.2472
Beltrán, J. J., Barrero, C. A., Punnoose, A. (2015). Understanding the role of iron in the magnetism of Fe doped ZnO nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. 17: 15284. Doi: 10.1039/C5CPO1408E
Binasch, G., Grünberg, P., Saurenbach, F., Zinn, W. (1989). Enhanced magnetoresistance in layered magnetic structures with antiferromagnetic interlayer exchange. Physical Review B. 39 (7): 4828-4830. Doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.39.4828
Casanova, A., Pérez-Alcázar, A., Aguirre, W.R., Salazar, D., Zamora, L.E. (2018). Effect of the Milling Conditions on the Properties of ZnO Doped with Fe. Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism. 31 (4): 4021-4028. Doi: 10.1007/s10948-018-4657-0
Chandrasekaran, E.G. (2017). Optical, electrical and ferromagnetic studies of ZnO:Fe diluted magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles for spintronic applications. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy. 186: 120-131R. Doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2017.05.065
Coey, J. M. D., Venkatesan, M., Fitzgerald, C. B. (2005). Donor impurity band exchange in dilute ferromagnetic oxides. Nature Materials. 4173: 173-179. Doi: 10.1038/nmat1310
Dietl, T., Ohno, H., Matsukura, F., Cibert, J., Ferrand, D. (2000). Zener Model Description of Ferromagnetism in Zinc-Blende Magnetic Semiconductors. Science. 287 (5455): 1019. Doi: 10.1126/science.287.5455.1019
Fan, L., Dongmei, J., Xueming, M. (2010). The influence of annealing on the magnetism of Fe doped ZnO prepared by mechanical alloying. Physica B: Condensed Matter. 405 (6): 1466. Doi: 10.1016/J.PHYSB.2009.12.010
Fert, A. & Campbell, I.A. (1968). Two-Current Conduction in Nickel. Phys. Rev. Lett. 21: 1190. Doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.21.1190
Ghosh, S. S., Choubey, C., Sil, A. (2019). Photocatalytic response of Fe,Co, Ni doped ZnObased diluted magnetic semiconductors for spintronics applications. Superlattices and Microstructures. 125: 271-280. Doi: 10.106/j.spmi.2018.10.028
Ghosh, S.S., Choubey, C., Sil, A. (2019). Photocatalytic response of Fe, Co, Ni doped ZnObased diluted magnetic semiconductors for spintronics applications. Superlattices and Microstructures. 125: 271-280. Doi: 10.2016/j-spmi.2018.10.028
Izumi, F. & Momma, K. (2007). Three-Dimensional Visualization in Powder Diffraction. Solid State Phenomena. 130: 15-20. Doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/SSP.130.15
Karmakar, D., Mandal, S.K., Kadam, R.M., Paulose, P.L., Rajarajan, A. K., Nath, T.K., Das, A.K., Dasgupta, I., Das, G.P. (2007). Ferromagnetism in Fe-doped ZnO nanocrystals: Experiment and theory. Physical Review B. 75: 144404. Doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.75.144404
Lin, Y., Jiang, D., Lin, F., Shi, W., Ma, X. (2007). Fe-doped ZnO magnetic semiconductor by mechanical alloying. Journal of Alloys and Compounds. 436 (1-2): 30. Doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.07.011
Loegel, B. & Gautier, F. (1971). Origine de la resistivite dans le cobalt et ses alliages dilues. J. Phys. Chem. Sol. 32: 2723. Doi: 10.1016/SOO22-3697(71)80364-5
Mishra, A.K. & Das, D. (2010). Investigation on Fe-doped ZnO nanostructures prepared by a chemical route. Materials Science and Engineering B. 171 (5): 5-10. Doi: 10.1016/j.mseb.2010.03.045
Moore, G.E. (1965). Cramming more components onto integrated circuits Electronics. 38 (8): 19.
Ohno, H. (1998). Making Nonmagnetic Semiconductors Ferromagnetic. Science. 281: 951. Doi: 10.1126/science.281.5379.951
Quesada, A., García, M.A., Costa-Krämer, J.L., Fernández, J.F., Martín-González, M., Hernando, A. (2007). Semiconductores magnéticos diluidos: materiales para la spintrónica. Revista española de física. 21 (1): 37-41
Ramos, J.E., Montero-Muñoz, M., Coaquira, J.A.H., Rodríguez-Páez, J. E. (2014). Evidence of a cluster glass-like behavior in Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Journal of Applied Physics. 115: 17E123. Doi: 10.1063/1.4864246
Sharma, P., Gupta, A., Owens, F.J., Inoue, A., Rao, K.V. (2004). Room temperature spintronic material Mn-doped ZnO revisited J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 282: 115-121. Doi: 10.1016/J.JMMM.2004.04.028
Sharma, P.A., Gupta, K.V., Rao, F.J., Owens, R., Sharma, R., Ahuja, J.M. Guillen, B., Johansson, B., Gehring, G.A. (2003). Ferromagnetism above room temperature in bulk and transparent thin films of Mn-doped ZnO. Nat. Mater. 2: 673. Doi: 10.1038/nmat984
Simões, C.B., de Sousa e Silvaa, R.L., Banerjeea, B., Franco Jr., P. (2019). Investigation of Fedoped room temperature dilute magnetic ZnO semiconductors. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing. 96: 122-126 Doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2019.02.021
Torrance, J.B., Shafer, M.W., McGuire, T. R. (1972). Bound Magnetic Polarons and the Insulator-Metal Transition in EuO. Phys. Rev. Lett. 29: 1168. Doi: 10.1103/pHYSrEVlETT.29.1168
Ueda, K., Tabata, H., Kawai, T. (2001). Magnetic and electric properties of transition-metal- doped ZnO films Appl. Phys. Lett. 79: 988. Doi: 10.1063/1.1384478
Wolf, S.A., Awschalom, D.D., Buhrman, R.A., Daughton, J. M., von. Molnár, S., Roukes, M. L.; Chtchelkanova, A.Y., Treger, D. M. (2001). Spintronics: a spin-based electronics vision for the future. Science. 294: 1488. Doi: 10.1126/science.1065389
Zamora, L.E., Paz, J. C., Piamba, J. F., Tabares, J. A., Pérez-Alcázar, G. A. (2015). A Mössbauer and magnetic study of ball milled Fe-doped ZnO Powders. Hyperfine Interact. 232: 111-118. Doi: 10.1007/s10751-015-1155-7
Zener, C. (1951). Interaction Between the d Shells in the Transition Metals. Physical Review. 81440: 440-444. Doi: 10.1103/pHYSrEV.81.440

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Derechos de autor 2020 Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales