Resumen
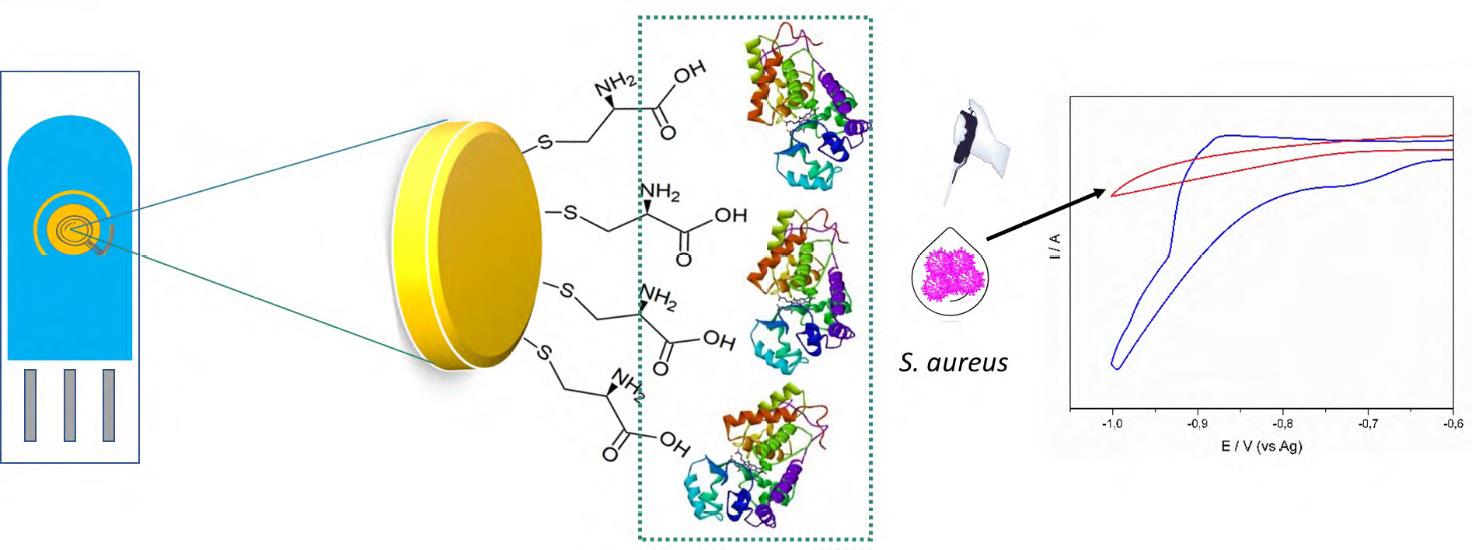
Se desarrolló un novedoso método electroquímico para la detección rápida y analítica de Staphylococcus aureus en cultivos y muestras de leche enriquecidas con peróxido de hidrógeno (H2O2) mediante el consumo de péroxido por electrodos serigrafiados de oro (ESO) modificados con cisteína y peroxidasa de pasto Guinea (PPG). La peroxidasa de las hojas del pasto Guinea, con una actividad específica de 470 U mg-1, se inmovilizó sobre la superficie de los ESO previamente modificada con cisteína. Los voltamperogramas cíclicos de los ESO modificados con PPG y cisteína en presencia de ferrocianuro de potasio como sonda redox exhibieron un incremento en la corriente de aproximadamente 5 % comparado con el electrodo sin modificar. El ESO modificado mostró una buena respuesta electrocatalítica en la reducción de H2O2. El medio de cultivo en presencia de 1x10-3 M de H2O2 registró una disminución en la corriente por la catalasa presente en S. aureus a un potencial de -780 mV. El ESO modificado pudo detectar S. aureus en un rango de concentraciones entre 3x102 and 3x108 UFC mL-1 con un límite de detección de 102 ufc mL-1, un tiempo de detección de ~20 min y una sensibilidad de 0,020 mA UFC-1.
Referencias
Alexandre, D.L, Melo, A.A, Furtado, R.F, Borges, M.F, Figueiredo, E.A, Biswas, A, Cheng, H.N, Alves, C. (2018). A rapid and specific biosensor for Salmonella typhimurium detection in milk. Food and Biop Techn. 11: 748-756.
Amiri, M., Bezaatpour, A., Jafari, H., Boukherroub, R., Szunerits, S. (2018). Electrochemical methodologies for the detection of pathogens. ACS Sensors. 6: 1059-1086.
Bradford, M.M. (1976). A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. 254: 248-254.
Castillo, J., Ferapontova, E., Hushpulian, D., Tasca, F., Tishkov, V., Chubar, Gorton, L. (2006). Direct electrochemistry and bioelectrocatalysis of H2O2 reduction of recombinant tobacco peroxidase on graphite. Effect of peroxidase single-point mutation on Ca2+-modulated catalytic activity. J Electroanal Chem. 588: 112-121.
Castillo, J. J., Rindzevicius, T., Wu, K., Schmidt, M. S., Janik, K. A., Boisen, A., Castillo-León, J. (2014). Synthesis and characterization of covalent diphenylalanine nanotube-folic acid conjugates. J Nanop Res. 16: 2524-2532.
Centeno, D. A., Solano, X. H., Castillo, J. J. (2017). A new peroxidase from leaves of Guinea grass (Panicum maximum): A potential biocatalyst to build amperometric biosensors. Bioelectrochemistry. 116: 33-38.
Chen, S., Yuan, R., Chai, Y., Xu, L., Wang, N., Li, X., Zhang, L. (2006). Amperometric hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on the immobilization of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) on the layerby-layer assembly films of gold colloidal nanoparticles and toluidine blue. Electroanalysis. 18: 471-477.
Escamilla-Gómez, V., Campuzano, S., Pedrero, M., Pingarrón, J. M. (2007). Development of an amperometric immunosensor for the quantification of Staphylococcus aureus using selfassembled monolayer-modified electrodes as immobilization platforms. Electroanalysis. 19: 1476-1482.
Gao, F., Yuan, R., Chai, Y., Tang, M., Cao, S., Chen, S. (2007). Amperometric third-generation hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on immobilization of Hb on gold nanoparticles/cysteine/poly(p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid)-modified platinum disk electrode. Col Surf A: Physicochem Eng Asp. 295: 223-227.
Gao, F., Yuan, R., Chai, Y., Tang, M., Cao, S., Chen, S. (2007). Amperometric third-generation hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on immobilization of Hb on gold nanoparticles/cysteine/poly(p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid)-modified platinum diskelectrode. Col Surf A: Physicochem Eng Asp. 295: 223-227.
Han, D., Yan, Y., Wang, J., Zhao, M., Duan, X., Kong, L., Wu, H., Cheng, W., Min, X., Ding, S. (2019). An enzyme-free electrochemiluminesce aptasensor for the rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus by the quenching effect of MoS2-PtNPs-vancomycin to S2O8 2−/O2 system. Sensors Act. B: Chem. 288: 586-593.
HSI, M. (2014). Staphylococcus aureus can Produce Catalase Enzyme when React with Human Wbcs as a Source of H2O2 Productions in Human Plasma or Serum in the Laboratory. J Med Microbiol & Diag. 3: 3-4.
Lazcka, O., Campo, F. J. Del, Muñoz, F. X. (2007). Pathogen detection: A perspective of traditional methods and biosensors. Bios Bioelect. 22: 1205-1217.
Liebana, S., Lermo, A., Campoy, S., Cortes, M., Alegret, S., Pividori, A. (2009). Rapid detection of Salmonella in milk by electrochemical magneto-immunosensing. Bios Bioelect. 25: 510-513.
Liu, H., Li, H., Wu, T., Hao, T. (2017). Differences of Bactericidal Efficacy on Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacillus subtilis of Slightly and Strongly Acidic Electrolyzed Water. Food and Biop Techn. 10: 155-164.
Lin, Y., Chen, S., Chuang, Y., Lu, Y., Shen, T., Chang, C., Lin, C. (2008). Disposable amperometric immunosensing strips fabricated by Au nanoparticles-modified screen-printed carbon electrodes for the detection of foodborne pathogen Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biosens Bioelect. 23: 1832-1837.
Majumdar, T., Chakraborty, R., Raychaudhuri, U. (2013). Rapid Electrochemical Quantification of Food Borne Pathogen Staphylococcus aureus Based on Hydrogen Peroxide Degradation by Catalase . J Electrochem Soc. 160: G75-G78.
Muraoka, T. & Wesley, I. (2011). Time of Entry of Salmonella and Campylobacter into the Turkey Brooder House. Food and Biop Techn. 4: 616-623.
Nistor, C., Osvik, A., Davidsson, R., Rose, A., Wollenberger, U., Fiksdal, L. (2002). Detection of
Escherichia coli in water by culture-based amperometric and luminometric methods. Wat Sci Techn. 45: 191-199.
Niu, X., Si, Q., Chen, Y., Luo, R., Wang, H. (2018). A sortase A-immobilized mesoporous hollow carbon sphere-based Biosensor for detection of gram-positive bacteria. J Elect Mat. 47: 4124-4135.
Orduz, A. E., Gutiérrez, J. A., Blanco, S. I., Castillo, J. J. (2019). Amperometric detection of triclosan with screen-printed carbon nanotube electrodes modified with Guinea Grass (Panicum maximum) peroxidase. Universit Scient. 24: 363-379.
Pérez, F., Tryland, I., Mascini, M., Fiksdal, L. (2001). Rapid detection of Escherichia coli in water by a culture-based amperometric method. Anal Chim Acta, 427: 149-154.
Ranjbar, S. & Shahrokhian, S. (2018). Design and fabrication of an electrochemical aptasensor using Au nanoparticles/carbon nanoparticles/cellulose nanofibers nanocomposite for rapid and sensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Bioelectrochemistry. 123: 70-76.
Ren, J., Zhou, Y., Zhou, Y., Zhou, C., Li, Z., Lin, Q., Huang, X. (2015). A piezoelectric picroelectrode arrays system for real-time monitoring of bacterial contamination in fresh milk. Food and Biop Techn. 8: 228-237.
Rodríguez, A., Pina, D. G., Yélamos, B., Castillo León, J. J., Zhadan, G. G., Villar, Shnyrov, V. L. (2002). Thermal stability of peroxidase from the African oil palm tree Elaeis guineensis. Europ J Biochem. 269: 2584-2590.
Setterington, E. B. & Alocilja, E. C. (2011). Rapid electrochemical detection of polyaniline-labeled Escherichia coli O157:H7. Bios Bioelect. 26: 2208-2214.
Tan, F., Leung, P. H. M., Liu, Z. Bin, Zhang, Y., Xiao, L., Ye, W., Yang, M. (2011). A PDMS microfluidic impedance immunosensor for E. coli O157:H7 and Staphylococcus aureus detection via antibody-immobilized nanoporous membrane. Sens Actuat B: Chem. 159: 328-335.
Uribe, P. A., Ortiz, C. C., Centeno, D. A., Castillo, J. J., Blanco, S. I., Gutiérrez, J. A. (2019). Self-assembled Pt screen printed electrodes with a novel peroxidase Panicum maximum an zinc oxide nanoparticles for H2O2 detection. Col Surf A: Physicochem Eng Asp. 561: 18-24.
Velusamy, V., Arshak, K., Korostynska, O., Oliwa, K., Adley, C. (2010). An overview of foodborne pathogen detection: In the perspective of biosensors. Biotech Adv. 28: 232-254.
Villamizar, E. N., Ríos, C. A., Castillo, J. J. (2016). A hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on the immobilization of the highly stable royal palm tree peroxidase (Roystonea regia) with chitosan and glutaraldehyde on screen-printed graphene. J Mex Chem Soc. 60: 135-140.
Wang, Y., Ye, Z., Ying, Y. (2012). New trends in impedimetric biosensors for the detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Sensors. 12: 3449-3471.
Wei, X., Wang, Z., Xia, Y., Wu, S., Duan, N., Jia, F. (2014). Impedimetric aptasensor for Staphylococcus aureus based on nanocomposite prepared from reduced graphene oxide and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta. 181: 967-974.
Xu, L., Liang, W., Yang, X., Jia, N., Zuo, X., Liu, G. (2018). An ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor for the detection of mecA gene in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens. Bioelect. 99: 424-430.
Xu, S. (2012). Electromechanical biosensors for pathogen detection. Microchim Acta. 178: 3-4.
Yue, H., Zhou, Y., Wang, P., Wang, X., Wang, Z., Wang, L., Fu, Z. (2016). A facile label-free electrochemiluminescent biosensor for specific detection of Staphylococcus aureus utilizing the binding between immunoglobulin G and protein A. Talanta, 153: 401-406.

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Derechos de autor 2020 Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales