Resumen
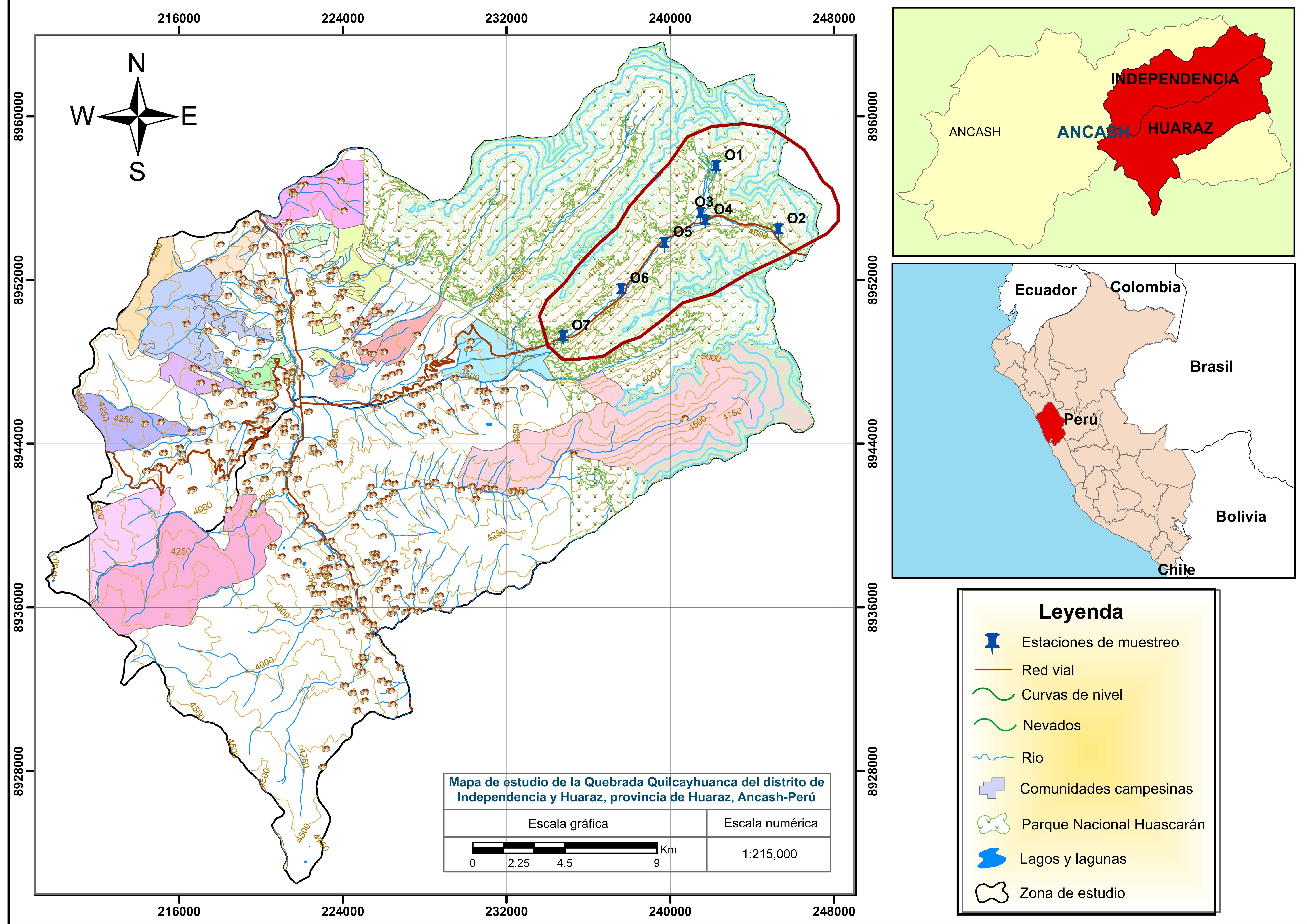
El retroceso glaciar expone rocas sulfuradas y promueve la meteorización in situ, por lo que pueden presentarse condiciones de pH ácido y altas concentraciones de metales en el agua, los sedimentos y el suelo. El objetivo de este estudio fue evaluar el impacto de la acidificación debida al retroceso glaciar en la calidad del agua de la quebrada Quilcayhuanca en Áncash, Perú, utilizando la planta Lemna minor y el cladócero Daphnia magna en ensayos de ecotoxicidad. Se determinaron en siete puntos de muestreo los parámetros físico-químicos y la toxicidad del agua superficial (AS) y del elutriado del sedimento (ES) mediante bioensayos con L. minor y D. magna. En los análisis físicoquímicos se obtuvo un pH ≤4, una conductividad eléctrica (CE) de 380 μS/cm y una turbidez de 113 UNT. Las concentraciones de cadmio (Cd), plomo (Pb), Níquel (Ni) y zinc (Zn) superaron el estándar de calidad ambiental (ECA) para agua de Perú, en tanto que las de As, Cd, cobre (Cu), Pb y Zn superaron la normativa canadiense de sedimentos, y la de Cd y As, el ECA para suelo de Perú. Se determinaron los valores de la concentración de AS y ES, con una clorosis de ≤6,25 % y 12,5 %, respectivamente, (confirmar con los autores) y del efecto por exposición al contaminante (NOEC); se registró la formación de hojas nuevas y el número total de frondas de L. minor en los siete puntos de muestreo, así como el peso seco de L. minor en uno de los puntos. En el ensayo con D. magna se determinó una concentración efectiva media para la inmovilidad (CE50-48h) de 43,55 % a 51,14%, y una concentración letal media (CL50-48h) de 50 % a 57,66 % en los ensayos con ES y AS. La ecotoxicidad en el AS y el ES debida al retroceso glaciar de la quebrada Quilcayhuanca se asoció con el pH y la presencia de metales pesados.
Referencias
Akindele, E. O., Omisakin, O. D., Oni, O. A., Aliu, O. O., Omoniyi, G. E., Akinpelu, O. T. (2020). Heavy metal toxicity in the water column and benthic sediments of a degraded tropical stream. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 190, 110153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110153
Baraer, M., Mark, B. G., McKenzie, J. M., Condom, T., Bury, J., Huh, K. I., (mencionar hasta 20 autores)... Rathay, S. (2012). Glacier recession and water resources in Peru’s Cordillera Blanca. Journal of Glaciology, 58 (207), 134-150. https://doi.org/10.3189/2012JoG11J186
Brighenti, S., Tolotti, M., Bruno, M. C., Wharton, G., Pusch, M. T., Bertoldi, W. (2019). Ecosystem shifts in Alpine streams under glacier retreat and rock glacier thaw: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 675, 542-559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.221
Caja-Molina, A. V. & Iannacone, J. (2021). Evaluación del riesgo ambiental por petróleo crudo en las especies acuáticas Lemna minor, Daphnia magna y Danio rerio. Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales, 45 (176), 777-794. https://doi.org/10.18257/raccefyn.1398
Cauvy-Fraunié, S., Espinosa, R., Andino, P., Jacobsen, D., Dangles, O. (2015). Estructura y dinámica de metacomunidades de invertebrados en una red de arroyos glaciares andinos frente al cambio climático. PloS uno, 10 (8), e0136793. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0136793
Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment - CCME (1999). Canadian Sediment Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life. Canadian environmental quality guidelines. https://ccme.ca/en/resources#
Chen, L., Zhang, G., Zeng, Y., Ren, Z. (2012). Influences of temperature, pH and turbidity on the behavioral responses of Daphnia magna and Japanese Medaka (Oryzias latipes) in the biomonitor. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 13, 80-86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2012.01.007
Cui, R., Kwak, J. I., An, Y. J. (2018). Comparative study of the sensitivity of Daphnia galeata and Daphnia magna to heavy metals. Ecotoxicology and environmental safety, 162, 63-70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.06.054
Daud, M. K., Ali, S., Abbas, Z., Zaheer, I. E., Riaz, M. A., Malik, A., ... Zhu, S. J. (2018). Potential of duckweed (Lemna minor) for the phytoremediation of landfill leachate. Journal of Chemistry, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3951540
Duodu, G. O., Goonetilleke, A., Ayoko, G. A. (2017). Potential bioavailability assessment, source apportionment and ecological risk of heavy metals in the sediment of Brisbane River estuary, Australia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 117(1-2), 523-531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.02.017
ECA (2017a). Estándares de Calidad Ambiental para Agua Decreto Supremo N° 004-2017-MINAM, Perú. https://sinia.minam.gob.pe/normas/aprueban-estandares-calidad-ambiental-eca-aguaestablecen-disposiciones
ECA (2017b). Estándares de Calidad Ambiental para Suelos Decreto Supremo N° 011-2017-MINAM, Perú. https://sinia.minam.gob.pe/normas/aprueban-estandares-calidad-ambiental-eca-suelo-0
Elbana, T. A., Selim, H. M., Akrami, N., Newman, A., Shaheen, S. M., Rinklebe, J. (2018). Freundlich sorption parameters for cadmium, copper, nickel, lead, and zinc for different soils: Influence of kinetics. Geoderma, 324, 80-88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.03.019
Fortner, S. K., Mark, B. G., McKenzie, J. M., Bury, J., Trierweiler, A., Baraer, M., (mencionar hasta 20 autores)... Munk, L. (2011). Elevated stream trace and minor element concentrations in the foreland of receding tropical glaciers. Applied Geochemistry, 26 (11), 1792-1801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.06.003
Gordon, R. P., Lautz, L. K., McKenzie, J. M., Mark, B. G., Chávez, D., Baraer, M. (2015). Sources and pathways of stream generation in tropical proglacial valleys of the Cordillera Blanca, Peru. Journal of Hydrology, 522, 628-644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.01.013
Grande, J. A., Loayza-Muro, R., Alonso-Chaves, F. M., Fortes, J. C., Willems, B., Sarmiento, A. M., (mencionar hasta 20 autores) ... Luís, A. T. (2019). The Negro River (Ancash-Peru): A unique case of water pollution, three environmental scenarios and an unresolved issue. Science of The Total Environment, 648, 398-407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.068
Instituto Nacional de Investigación de Glaciares y Ecosistema de Montaña- INAIGEM. (2018). (¿Nombre del documento consultado?). https://repositorio.inaigem.gob.pe/handle/16072021/57
Jaiswal, A., Verma, A., Jaiswal, P. (2018). Detrimental effects of heavy metals in soil, plants, and aquatic ecosystems and in humans. Journal of Environmental Pathology, Toxicology and Oncology, 37(3), 183-197. https://doi.org/10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.2018025348
Król, A., Mizerna, K., Bożym, M. (2020). An assessment of pH-dependent release and mobility of heavy metals from metallurgical slag. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 384, 121502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121502
Lee, S. H., Kim, I., Kim, K. W., Lee, B. T. (2015). Ecological assessment of coal mine and metal mine drainage in South Korea using Daphnia magna bioassay. SpringerPlus, 4 (1), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-015-1311-1
Leggat, M. S., Owens, P. N., Stott, T. A., Forrester, B. J., Déry, S. J., Menounos, B. (2015). Hydro‐meteorological drivers and sources of suspended sediment flux in the pro‐ glacial zone of the retreating Castle Creek Glacier, Cariboo Mountains, British Columbia, Canada. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 40(11), 1542-1559. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.3755
Lin, Q. & Xu, S. (2020). Co-transport of heavy metals in layered saturated soil: characteristics and simulation. Environmental Pollution, 261, 114072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114072
Loganathan, P., Vigneswaran, S., Kandasamy, J., Bolan, N. S. (2014). Removal and recovery of phosphate from water using sorption. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 44 (8), 847-907. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2012.741311
López-Moreno, J. I., Valero-Garcés, B., Mark, B., Condom, T., Revuelto, J., Azorín-Molina, C., (mencionar hasta 20 autores)... Alejo-Cochachin, J. (2017). Hydrological and depositional processes associated with recent glacier recession in Yanamarey catchment, Cordillera Blanca (Peru). Science of the Total Environment, 579, 272-282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.107
Lu, Q., Zhang, T., Zhang, W., Su, C., Yang, Y., Hu, D., Xu, Q. (2018). Alleviation of cadmium toxicity in Lemna minor by exogenous salicylic acid. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 147, 500-508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.09.015.
Magnússon, R., Cammeraat, E., Lücke, A., Jansen, B., Zimmer, A., Recharte, J. (2020). Influence of glacial sediments on the chemical quality of surface water in the Ulta valley, Cordillera Blanca, Peru. Journal of hydrology, 587, 125027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125027
Mark, B. G., McKenzie, J. M., Gómez, J. (2005). Hydrochemical evaluation of changing glacier meltwater contribution to stream discharge: Callejon de Huaylas, Peru/Evaluation hydrochimique de la contribution évolutive de la fonte glaciaire à l’écoulement fluvial: Callejon de Huaylas, Pérou. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 50 (6), ¿pp?. https://doi.org/10.1623/hysj.2005.50.6.975
Mesquita, A. F., Abrantes, N., Campos, I., Nunes, C., Coimbra, M. A., Gonçalves, F. J., (mencionar hasta 20 autores)... Gonçalves, A. M. (2022). Effects of wildfire ash on the growth and biochemical profiles of the aquatic macrophyte Lemna minor. Aquatic Toxicology, 250, 106245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2022.106245
Miranda, L. S., Ayoko, G. A., Egodawatta, P., Goonetilleke, A. (2022). Adsorption-desorption behavior of heavy metals in aquatic environments: Influence of sediment, water and metal ionic properties. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 421, 126743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126743
Miranda, L. S., Ayoko, G. A., Egodawatta, P., Hu, W. P., Ghidan, O., Goonetilleke, A. (2021). Physico-chemical properties of sediments governing the bioavailability of heavy metals in urban waterways. Science of The Total Environment, 763, 142984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142984
Nasnodkar, M.R. & Nayak, G.N. (2019). Geochemical speciation of selected metals to understand source, bioavailability and toxicity in mudflat core sediments of a tropical (Vaghotan) estuary, India. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 31, 100803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2019.100803
Navas, A., Lizaga, I., Gaspar, L., Latorre, B., Dercon, G. (2020). Unveiling the provenance of sediments in the moraine complex of Aldegonda Glacier (Svalbard) after glacial retreat using radionuclides and elemental fingerprints. Geomorphology, 367, 107304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2020.107304
OCDE. (2004). Guideline for testing of chemicals. Test No. 202: Daphnia sp. Acute Immobilisation Test. https://www.oecdilibrary.org/docserver/9789264069947-en.pdf?expires=1621114445&id=id&accname=guest&checksum=784CB027CAFE3363FE66D15BAAA3B9C6
OCDE. (2006). Guideline for testing of Chemicals. Test No. 221: Lemna sp. Growth Inhibition Test https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/docserver/9789264016194-en.pdf?expires=1621114790&id=id&accname=guest&checksum=9EAE42390B8516E21F87321CEB26DCCF
Outa, J. O., Kowenje, C. O., Plessl, C., Jirsa, F. (2020). Distribution of arsenic, silver, cadmium, lead and other trace elements in water, sediment and macrophytes in the Kenyan part of Lake Victoria: spatial, temporal and bioindicative aspects. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27 (2), 1485-1498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06525-9
Pérez, E. & Hoang, T. C. (2017). Chronic toxicity of binary‐metal mixtures of cadmium and zinc to Daphnia magna. Environmental toxicology and chemistry, 36 (10), 2739-2749. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3830
Pérez, E. & Hoang, T. C. (2018). Responses of Daphnia magna to chronic exposure of cadmium and nickel mixtures. Chemosphere, 208, 991-1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.063
Qin, L., Huang, Q., Wei, Z., Wang, L., Wang, Z. (2014). The influence of hydroxylfunctionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes and pH levels on the toxicity of lead to Daphnia magna. Environmental toxicology and pharmacology, 38 (1), 199-204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2014.05.016
Reyes-Nolasco, A. W. (2018). Contaminación por metales pesados de aguas y suelos en la microcuenca quilcayhuanca; su relación con la litología y el contexto del cambio climático; Huaraz Ancash Perú 2014-2015. http://repositorio.unasam.edu.pe/handle/UNASAM/2381
Rodrigues, G. Z. P., Finkler, M., Garcia, A. L. H., Gehlen, G. (2020). Evaluation of transgenerational effects caused by metals as environmental pollutants in Daphnia magna. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192 (12), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08713-4
Sackey, L. N., Kočí, V., van Gestel, C. A. (2020). Ecotoxicological effects on Lemna minor and Daphnia magna of leachates from differently aged landfills of Ghana. Science of the Total Environment, 698, 134295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134295
Sackey, L. N., Mocová, K. A., Petrová, Š., Kočí, V. (2021). Toxicity of wood leachate to algae Desmodesmus subspicatus and plant Lemna minor. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(47), 67150-67158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15319-x
Salesa, B., Sancho, E., Ferrando-Rodrigo, M. D., Torres-Gavilá, J. (2022). The prochloraz chronic exposure to Daphnia magna derived in biochemical alterations of F0 generation daphnids and malformed F1 progeny. Chemosphere, 307, 135848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135848
Santofimia, E., López-Pamo, E., Palomino, E. J., González-Toril, E., Aguilera, Á. (2017). Acid rock drainage in Nevado Pastoruri glacier area (Huascarán National Park, Perú): hydrochemical and mineralogical characterization and associated environmental implications. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24 (32), 25243-25259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0093-0
Schauwecker, S., Rohrer, M., Acuña, D., Cochachin, A., Dávila, L., Frey, H., ... & Vuille, M. (2014). Climate trends and glacier retreat in the Cordillera Blanca, Peru, revisited. Global and Planetary Change, 119, 85-97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2014.05.005
United States Environmental Protection Agency- EPA. (1994a). “Method 200.8: Determination of Trace Elements in Waters and Wastes by Inductively Coupled Plasma - Mass Spectrometry,” Revision 5.4. Cincinnati, OH. https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-06/documents/epa-200.8.pdf
United States Environmental Protection Agency- EPA. (1996). “Method 3050-B: Acid Digestion of sediments, sludges, and soil”. Revisión 2. https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-06/documents/epa-3050b.pdf
United States Environmental Protection Agency- EPA. (1994b). “Method 200.7 Revision 4.4: Acid Digestion of Sediments, Sludges, and Soils / Determination of Metals and Trace Elements in Water and Wastes by Inductively Coupled Plasma – Atomic Emission Spectrometry (ICP-AES)”. https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-08/documents/method_200-7_rev_4-4_1994.pdf
United States Environmental Protection Agency- EPA. (2018). “SW-846 Method 6010D. Inductively Coupled Plasma – Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES)”. Revision 5. https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-12/documents/6010d.pdf
Valverde, G. M., Lázaro, J. C. T., Infantes, W. H. J. (2018). Variación del pH en aguas superficiales debido a drenajes ácidos de roca en la Subcuenca Quillcay, Huaraz, Ancash. Revista de Glaciares y Ecosistemas de Montaña, 5, 12-12. https://doi.org/10.36580/rgem.i5.57-68
Veettil, B. K. & Kamp, U. (2019). Global disappearance of tropical mountain glaciers: observations, causes, and challenges. Geosciences, 9 (5), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9050196
Vidal, T., Pereira, J. L., Abrantes, N., Soares, A. M., Gonçalves, F. (2012). Ecotoxicological assessment of contaminated river sites as a proxy for the water framework directive: an acid mine drainage case study. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 223(9), 6009-6023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1335-x
Vuille, M., Carey, M., Huggel, C., Buytaert, W., Rabatel, A., Jacobsen, D., ... Sicart, J. E. (2018). Rapid decline of snow and ice in the tropical Andes–Impacts, uncertainties and challenges ahead. Earth-science Reviews, 176, 195-213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.09.019
Žaltauskaitė, J. & Vaitonytė, I. (2016). Toxicological assessment of closed municipal solid-waste landfill impact on the environment. [Toksikologinis uždaryto municipalinių atliekų sąvartyno poveikio aplinkai vertinimas] Environmental Research, Engineering and Management, 72(4), 8-16. https://doi:10.5755/j01.erem.72.4.16555
Zicari, M. A., d’Aquino, L., Paradiso, A., Mastrolitti, S., Tommasi, F. (2018). Effect of cerium on growth and antioxidant metabolism of Lemna minor L. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 163, 536-543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.113
Zhang, Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, Z., Liu, Ch., Sun, C., Zhang, W., Marhaba, T. (2018). pH effect on heavy metal release from a polluted sediment. Journal of Chemistry, 2018, 7597640. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7597640
Ziegler, P., Sree, K. S., Appenroth, K. J. (2018). Duckweed biomarkers for identifying toxic water contaminants? Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(15), 14797-14822. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3427-7

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Derechos de autor 2023 Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales