Resumen
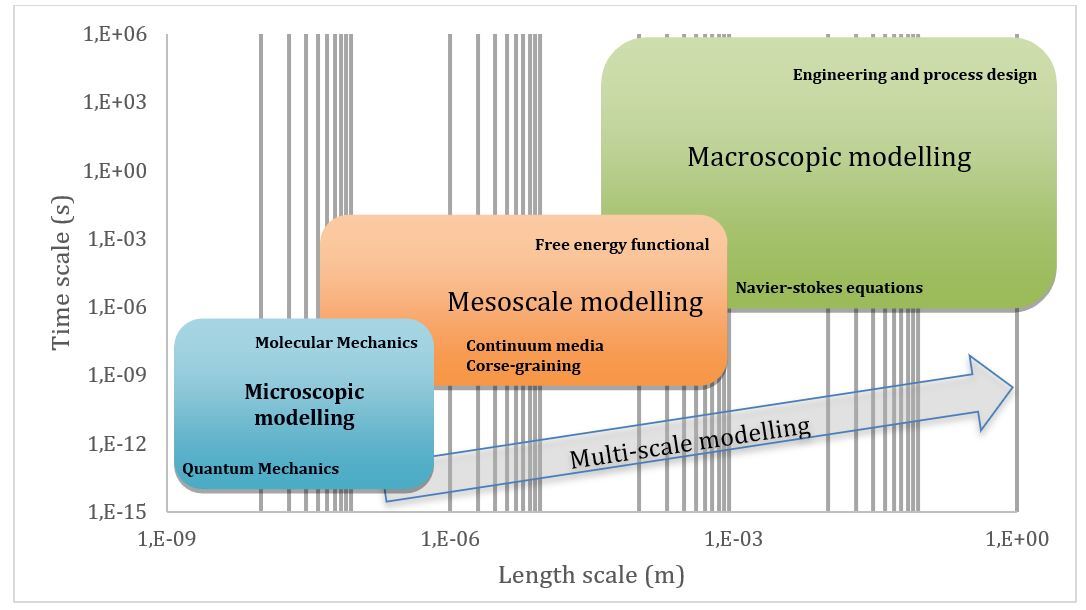
Este trabajo trata sobre el modelado multiescala de procesos químicos. A pesar de la existencia de muy buenos modelos para procesos químicos desde el punto de vista macroscópico, estos pueden verse limitados por el uso de coeficientes de transporte y transferencia mal estimados que reducen la precisión para un buen desarrollo tecnológico. Incluso si los modelos se basan en relaciones fundamentales, existe una conexión poco clara entre su coeficiente de transporte y la dinámica molecular. Los modelos microscópicos pueden modelar varios fenómenos con extrema precisión, que tuvieron lugar en tamaños atómicos o moleculares. Sin embargo, se necesita mucho tiempo de cálculo para crear un vínculo entre la microescala y la macroescala. Por tanto, la forma de vincularlos no es directa y se estudia con detalle en este trabajo.
Referencias
Alvarez, H., Lamanna, R., Vega, P., Revollar, S. (2009). Metodología para la obtención de modelos semifísicos de base fenomenológica aplicada a una sulfitadora de jugo de caña de azúcar. RIAI - Revista Iberoamericana de Automatica e Informatica Industrial, 6(3), 10-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1697-7912(09)70260-2
Aris, R. (1994). Mathematical modelling techniques. Dover Publications, New York. Atehortúa, P., Álvarez, H., Orduz, S. (2007). Modeling of growth and sporulation of Bacillus thuringiensis in an intermittent fed batch culture with total cell retention. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 30(6), 447-456. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00449-007-0141-0
Auriault, J.L. (2016). Cattaneo-Vernotte equation versus Fourier thermoelastic hyperbolic heat equation. International Journal of Engineering Science, 101, 45-49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijengsci.2015.12.002
Avalos, J.B., Mackie, a. D. (1999). Dynamic and transport properties of dissipative particle dynamics with energy conservation. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 111(11), 5267. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.479780
Basmadjian, D., Farnood, R., Basmadjian, D. (2007). The art of modeling in science and engineering with Mathematica / (Segunda edición). Chapman & Hall/CRC.
Bell, J., García, A., Williams, S. (2007). Numerical methods for the stochastic Landau-Lifshitz Navier-Stokes equations. Physical Review E, 76(1), 016708. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.76.016708
Camargo, Di., De La Torre, J.A., Duque-Zumajo, D., Español, P., Delgado-Buscalioni, R., Chejne, F. (2018). Nanoscale hydrodynamics near solids. Journal of Chemical Physics, 148(6), 1-21. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5010401
Camargo-Trillos, D. (2017a). Mesoscale model of mass and momentum transport in nanopores. Universidad Nacional de Colombia. Camargo-Trillos, D. (2017b). Mesoscale Model of Mass and Momentum Transport in Nanopores. Universidad Nacional de Colombia-sede Medellín.
Cao, X., Xu, G., Li, Y., Zhang, Z. (2005). Aggregation of Poly (ethylene oxide)−Poly(propylene oxide) Block Copolymers in Aqueous Solution: DPD Simulation Study. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 109(45), 10418-10423. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp053636r
David, M., Álvarez, H., Ocampo-Martínez, C., Sánchez-Peña, R. (2020). Dynamic modelling of alkaline self-pressurized electrolyzers: a phenomenological-based semiphysical approach. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 45(43), 22394-22407. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJHYDENE.2020.06.038
de Zárate, J.M.O., Sengers, J.V. (Eds.) (2006). Hydrodynamic Fluctuations in Fluids and Fluid Mixtures. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-044451515-5/50005-3
Donev, A., Bell, J., García, A., Alder, B. (2010a). A Hybrid Particle-Continuum Method for Hydrodynamics of Complex Fluids. Multiscale Modeling & Simulation, 8(3), 871-911. https://doi.org/10.1137/090774501
Donev, A., Vanden-Eijnden, E., García, A., Bell, J. (2010b). On the accuracy of finite-volume schemes for fluctuating hydrodynamics. Communications in Applied Mathematics and Computational Science, 5(2), 149-197. https://doi.org/10.2140/camcos.2010.5.149
Du, C., Ji, Y., Xue, J., Hou, T., Tang, J., Lee, S.-T., Li, Y. (2015). Morphology and Performance of Polymer Solar Cell Characterized by DPD Simulation and Graph Theory. Scientific Reports, 5(1), 16854. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16854
Einstein, A. (1905). On the motion of small particles suspended in liquids at rest required by the molecular kinetic theory of heat. Annals Physics, 17, 549-560.
Ellero, M., Español, P. (2018). Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition) Everything you always wanted to know about SDPD ⋆(⋆but were afraid to ask )∗. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 39(1), 103-124.
Ellero, M., Serrano, M., Español, P. (2007). Incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Journal of Computational Physics, 226(2), 1731-1752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2007.06.019
Español, P. (1993). Force autocorrelation function in Brownian motion theory. Journal of Chemical Physics, 98, 574-580.
Español, P. (1995). Hydrodynamics from dissipative particle dynamics. Physical Review E, 52(2), 1734-1742.
Español, P., Donev, A. (2015). Coupling a nano-particle with isothermal fluctuating hydrodynamics: Coarse-graining from microscopic to mesoscopic dynamics. Journal of Chemical Physics, 143(23). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4936775
Español, P., Revenga, M. (2003). Smoothed dissipative particle dynamics. Physical Review E, 67(2), 026705. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.67.026705
Español, P., Serrano, M., Öttinger, H. (1999). Thermodynamically Admissible Form for Discrete Hydrodynamics. Physical Review Letters, 83(22), 4542-4545. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.83.4542
Español, P., Serrano, M., Zúñiga, I. (1997). Coarse-graining of a fluid and its relation with dissipative particle dynamics and smoothed particle dynamics. International Journal of Modern Physics, 8(4), 899-908.
Espanol, P., Warren, P. (1995). Statistical mechanics of dissipative particle dynamics. EPL (Europhysics Letters), 30, 191-196.
Evans, D. J., Morriss, G. (2008). Statistical mechanics of Nonequilibrium Liquids (Second edition). Cambridge University Press.
Green, M. S. (1954). Markoff Random Processes and the Statistical Mechanics of Time-Dependent Phenomena. II. Irreversible Processes in Fluids. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 22(3), 398. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1740082
Groot, S. R., Mazur, P. (1984). Non-equilibrium Thermodynamics. Dover Publications, New York. Hangos, K., Cameron, I. (2001). Process modelling and model analysis / K.M. Hangos, I.T. Cameron. Academic Press.
Hoogerbrugge, P., Koelman, J. (1992). Simulating microscopic hydrodynamic phenomena with dissipative particle dynamics. EPL (Europhysics Letters), 19, 155-160.
Hoyos, E., López, D., Álvarez, H. (2016). A phenomenologically based material flow model for friction stirs welding. Materials & Design, 111, 321-330. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATDES.2016.09.009
Irving, J.H., Kirkwood, J.G. (2004). The Statistical Mechanical Theory of Transport Processes. IV. The Equations of Hydrodynamics. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 18(6), 817. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1747782
Kirkwood, J.G. (1947). The Statistical Mechanical Theory of Transport Processes II. Transport in Gases. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 15(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1746292
Kirkwood, J.G., Buff, F.P., Green, M.S. (2004). The Statistical Mechanical Theory of Transport Processes. III. The Coefficients of Shear and Bulk Viscosity of Liquids. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 17(10), 988. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1747099
Kubo, R. (1957). Statistical-Mechanical Theory of Irreversible Processes. I. General Theory and Simple Applications to Magnetic and Conduction Problems. Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 12(6), 570-586.
Landau, L.D., Lifshitz, E.M. (1959). Fluid Mechanics. Pergamon Press.
Landau, L.D., Lifshitz, E.M. (1987). Fluid Mechanics. In McGraw-Hill (Ed.), Image Rochester NY (Vol. 6, Issue 1). Pergamon Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/b138775
Lema-Pérez, L., García-Tirado, J., Builes-Montaño, C., Álvarez, H. (2019). Phenomenologicalbased model of human stomach and its role in glucose metabolism. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 460, 88–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtbi.2018.10.024
Ljung, L. (1999). System Identification: Theory for the User. Prentice Hall PTR. https://books.google.com.co/books?id=nHFoQgAACAAJ
López-Restrepo, S., García-Tirado, J., Álvarez, H. (2020). A Methodology for Identifying Phenomenological-Based Models using a Parameter Hierarchy. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 98(1), 213–224. https://doi.org/10.1002/CJCE.23500
Mansour, M., García, A., Lie, G., Clementi, E. (1987). Fluctuating hydrodynamics in a dilute gas. Physical Review Letters, 58(9), 874-877. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.58.874
Mashiyama, K., Mori, H. (1978). Origin of the Landau-Lifshitz hydrodynamic fluctuations in nonequilibrium systems and a new method for reducing the Boltzmann equation. Journal of Statistical Physics, 18(4), 385-407.
Monaghan, J.J. (2005). Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Reports on Progress in Physics, 68(8), 1703-1759. https://doi.org/10.1088/0034-4885/68/8/R01
Onsager, L. (1931). Reciprocal relations in irreversible processes. I. Physical Review, 36, 405–426. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.37.405
Ortega-Quintana, F.A., Álvarez, H., Botero-Castro, H.A. (2017). Enfrentando el modelado de bioprocesos: una revisión de las metodologías de modelado. Revista ION, 30(1), 73-90. https://doi.org/10.18273/revion.v30n1-2017006
Torre, J.A. De, Camargo, D., Español, P., Duque-Zumajo, D. (2019). Discrete hydrodynamics near solid walls: Non-Markovian effects and the slip boundary condition. Physical Review E, 100(6), 062133(24). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.100.062133
Vázquez-Quesada, A., Ellero, M., Español, P. (2009). Consistent scaling of thermal fluctuations in smoothed dissipative particle dynamics. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 130(3), 034901. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3050100
Vishnyakov, A., Talaga, D.S., Neimark, A.V. (2012). DPD Simulation of Protein Conformations: From α-Helices to β-Structures. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 3(21), 3081-3087. https://doi.org/10.1021/jz301277b
Voulgarakis, N.K., Satish, S., Chu, J.-W. (2010). Modelling the viscoelasticity and thermal fluctuations of fluids at the nanoscale. Molecular Simulation, 36(7-8), 552-559. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927022.2010.486832
Wendt, J.F., Anderson, J.D., Degroote, J., Degrez, G., Dick, E., Grundmann, R., Vierendeels, J. (2009). Computational fluid dynamics: An introduction. Computational Fluid Dynamics, 1-332. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-85056-4/COVER
Zuluaga-Bedoya, C., Ruiz-Botero, M., Ospina-Alarcón, M., García-Tirado, J. (2018). A dynamical model of an aeration plant for wastewater treatment using a phenomenological based semi-physical modeling methodology. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 117, 420-432. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPCHEMENG.2018.07.008
Zwanzig, R. (1960). Ensemble Method in the Theory of Irreversibility. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 33(5), 1338. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1731409
Zwanzig, R. (1961). Memory Effects in Irreversible Thermodynamics. Physics Review, 124(4), 983-992. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.124.983

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Derechos de autor 2023 Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales