Abstract
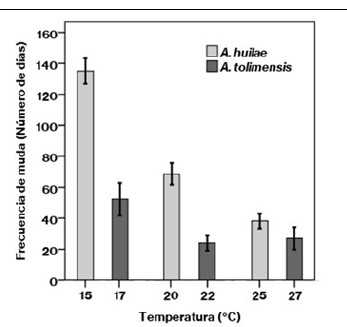
The heart rate and the molting frequency are two valuable parameters to determine the physiological state of animals, especially under the current environmental changes which are affecting their body temperature. Given the little information about these two physiological parameters in ectotherms, in this work, we determined the heart rate and molting frequency of the lizards Anolis huilae and A. tolimensis at three different temperatures under laboratory conditions, as well as their thermal sensitivity. The temperatures were 15, 20, and 25 °C for A. huilae and 17, 22, and 27 °C for A. tolimensis, selected according to the temperatures in the localities where they live in the department of Tolima: Juntas (A. huilae) and Llanitos (A. tolimensis). High temperatures increased the heart rate (A. huilae: from 53.3 beats per minute (bpm) at 17°C to 57.2 bpm at 27°C; A. tolimensis: from 45.1 bpm at 15°C to 50.6 bpm at 25°C) and decreased the molting frequency (A. huilae: from 135 days at 15°C to 38 days at 25°C; A. tolimensis: from 53 days at 17°C to 25 days at 27°C). Heart rate thermal sensitivity was low whereas the molting frequency was higher. As expected, increased environmental temperatures produced significant changes in animal functions that may be energetically expensive for the normal performance of lizards in natural conditions.
Keywords
References
Angilletta, M. J. (2001). Thermal and physiological constraints on energy assimilation in a widespread lizard (Sceloporus undulatus). Ecology. 82: 3044-3056. Doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(2001) 082[3044:TAPCOE]2.0.CO;2
Angilletta, M. J. (2006). Estimating and comparing thermal performance curves. Journal of Thermal Biology. 31: 541-545. Doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2006.06.002
Angilletta, M. J. (2009). Thermal adaptation: a theoretical and empirical synthesis. New York, United States: Oxford University Press. p. 289.
Angilletta, M. J., Niewiarowski, P. H., Navas, C. A. (2002). The evolution of thermal physiology in ectotherms. Journal of Thermal Biology. 27 (4): 249-268. Doi: 10.1016/S0306-4565(01)00094-8
Angilletta, M. J., Sears, M. W., Pringle, R. M. (2009). Spatial dynamics of nesting behavior: lizards shift microhabitats to construct nests with beneficial thermal properties. Ecology. 90(10): 2933-2939. Doi: 10.1890/08-2224.1
Ardila-Marín, D. A., Gaitán-Reyes, D. G., Hernández-Ruz, E. J. (2008). Biología reproductiva de una población de Anolis tolimensis (Sauria: Iguanidae) en los Andes colombianos. Caldasia. 30 (1): 151-159.
Aubret, F., Tort, M., Blanvillain, G. (2013). A non-invasive method of measuring heart rates in small reptiles and amphibians. Herpetological Review. 44: 421-423.
Bejarano-Bonilla, D. A. & Bernal-Bautista, M. H. (2019). Patrón de actividad diaria y de temperaturas ambientales y microambientales en una población de la lagartija endémica colombiana Anolis huilae (Squamata, Dactyloidae). Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales. 43 (166): 38-43. Doi: 10.18257/raccefyn.687
Bennett, A. F. (1972). The effect of activity on oxygen consumption, oxygen debt, and heart rate in the lizards Varanus gouldii and Sauromalus hispidus. Journal of Comparative Physiology. 79 (3): 259-280. Doi: 10.1007/BF00694220
Bennett, A. F. & Dawson, W. R. (1976). Biology of the Reptilia: Metabolism. New York, United States: New York Academic Press. p. 373.
Boulenger, G. A. (1908). Description of new batrachians and reptiles discovery by Mr. M.C. Palmer in south-western Colombia. Annals and Magazine of Natural History. 8 (2): 515-522.
Bustard, H. R. & Maderson, P. F. A. (1965). The eating of shed epidermal material in squamate reptiles. Herpetologica. 21(4): 306-308.
Butler, P. J., Green, J. A., Boyd, I. L., Speakman, J. R. (2004). Measuring metabolic rate in the field: the pros and cons of the doubly labelled water and heart rate methods. Functional Ecology. 18 (2): 168-183. Doi: 10.1111/j.0269-8463.2004.00821.x
Carvajal-Cogollo, J. E. & Urbina-Cardona, J. N. (2008). Patrones de diversidad y composición de reptiles en fragmentos de bosque seco tropical en Córdoba, Colombia. Tropical Conservation Science. 1 (4): 397-416. Doi: 10.1177/194008290800100407
Diele-Viegas, L. M., Vitt, L. J., Sinervo, B., Colli, G. R., Werneck, F. P., Miles, D. B., Pontes, E. (2018). Thermal physiology of Amazonian lizards (Reptilia: Squamata). PloS One. 13 (3): e0192834. Doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192834
Du, W. G., Ye, H., Zhao, B., Warner, D. A., Shine, R. (2010a). Thermal acclimation of heart rates in reptilian embryos. PLoS One. 5 (12): e15308. Doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015308
Du, W. G., Zhao, B., Shine, R. (2010b). Embryos in the fast lane: high-temperature heart rates of turtles decline after hatching. PLoS One. 5 (3): e9557. Doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009557
Dzialowski, E. M. & O’Connor, M. P. (2001). Thermal time constant estimation in warming and cooling ectotherms. Journal of Thermal Biology. 26 (3): 231-245. Doi: 10.1016/S0306-4565(00)00050-4
Gallego, C. A., Castro, C. F., Torres, K. A., Forero, J. S. (2012). Relación uso de hábitat y ectoparasitismo en una población de Anolis antonii (Dactyloidae) en Llanitos, Tolima-Colombia. The Biologist. 10 (2): 99.
Gallego-Carmona, C. A., Castro-Arango, J. A., Bernal-Bautista, M. H. (2016). Effect of habitat disturbance on the body condition index of the Colombian endemic lizard Anolis antonii (Squamata: Dactyloidae). South American Journal of Herpetology. 11 (3): 183-188. Doi: 10.2994/SAJH-D-16-00020.1
Green, J. A. (2011). The heart rate method for estimating metabolic rate: review and recommendations. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology. 158 (3): 287-304. Doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2010.09.011
Grigg, G. C. & Seebacher, F. (1999). Field test of a paradigm: hysteresis of heart rate in thermoregulation by a free-ranging lizard (Pogona barbata). Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences. 266 (1425): 1291-1297. Doi: 10.1098/rspb.1999.0777
Grisales-Martinez, F. A., Velasco, J. A., Bolivar, W., Williams, E. E., Daza, J. M. (2017). The taxonomic and phylogenetic status of some poorly known Anolis species from the Andes of Colombia with the description of a nomen nudum taxon. Zootaxa. 4303 (2): 213-230. Doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.4303.2.2
Harwood, R. H. (1979). The effect of temperature on the digestive efficiency of three species of lizards, Cnemidophorus tigris, Gerrhonotus multicarinatus and Sceloporus occidentalis. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Physiology. 63 (3): 417-433. Doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(79)90613-3
Jørgensen, C. B. & Larsen, L. O. (1960). Hormonal control of moulting in amphibians. Nature. 185 (4708): 244-245. Doi: 10.1038/185244a0
Kruskal, W. H. & Wallis, W. A. (1952). Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. Journal of the American statistical Association. 47 (260): 583-621. Doi: 10.2307/2280779
Licht, P. (1965). Effects of temperature on heart rates of lizards during rest and activity. Physiological Zoology. 38 (2): 129-137.
Ling, J. K. (1972). Adaptive functions of vertebrate molting cycles. American Zoologist. 12 (1): 77-93. Doi: 10.1093/icb/12.1.77
Meyer, E. A., Cramp, R. L., Bernal, M. H., Franklin, C. E. (2012). Changes in cutaneous microbial abundance with sloughing: possible implications for infection and disease in amphibians. Diseases of aquatic organisms. 101 (3): 235-242. Doi: 10.3354/dao02523
Patrakov, S. V. & Kuranova, V. N. (2006). Variation of moulting activity in Lacerta agilis and Zootoca vivipara (Reptilia: Sauria: Lacertidae). In Proceedings of the 13th Congress of the Societas Europaea Herpetologica. 111: 113.
Piercy, J., Rogers, K., Reichert, M., Andrade, D. V., Abe, A. S., Tattersall, G. J., Milsom, W. K. (2015). The relationship between body temperature, heart rate, breathing rate, and rate of oxygen consumption, in the tegu lizard (Tupinambis merianae) at various levels of activity. Journal of Comparative Physiology B. 185 (8): 891-903. Doi: 10.1007/s00360-015-0927-3
Randall, D., Burggren, W., French, K. (2002). Eckert Fisiología Animal: mecanismos y adaptaciones (4th Edition). Madrid, España: Graw-Hill Interamericana. p. 802
Raske, M., Lewbart, G. A., Dombrowski, D. S., Hale, P., Correa, M., Christian, L. S. (2012). Body temperatures of selected amphibian and reptile species. Journal of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine. 43 (3): 517-521. Doi: 10.2307/41681870
Sabagh, L. T. & Carvalho-e-Silva, A. M. (2008). Feeding overlap in two sympatric species of Rhinella (Anura: Bufonidae) of the Atlantic Rain Forest. Revista Brasileira de Zoologia. 25 (2): 247-253. Doi: 10.1590/S0101-81752008000200013
Schofield, G., Bishop, C. M., Katselidis, K. A., Dimopoulos, P., Pantis, J. D., Hays, G. C. (2009). Microhabitat selection by sea turtles in a dynamic thermal marine environment. Journal of Animal Ecology. 78 (1): 14-21. Doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2656.2008.01454.x
Seebacher, F. (2000). Heat transfer in a microvascular network: the effect of heart rate on heating and cooling in reptiles (Pogona barbata and Varanus varius). Journal of Theoretical Biology. 203 (2): 97-109. Doi: 10.1006/jtbi.1999.1067
Seebacher, F. & Franklin, C. E. (2005). Physiological mechanisms of thermoregulation in reptiles: a review. Journal of Comparative Physiology B. 175 (8): 533-541. Doi: 10.1007/s00360-005-0007-1
Seebacher, F. & Grigg, G. (2001). Changes in heart rate are important for thermoregulation in the varanid lizard Varanus varius. Journal of Comparative Physiology B. 171 (5): 395-400. Doi: 10.1007/s003600100188
Semlitsch, R. D. (1979). The influence of temperature on ecdysis rates in snakes (genus Natrix) (Reptilia, Serpentes, Colubridae). Journal of Herpetology. 13 (2): 212-214. Doi: 10.2307/1563932
Smith, G. C. (1976). Ecological energetics of three species of ectothermic vertebrates. Ecology. 57 (2): 252-264. Doi: 10.2307/1934814
Stefano, F. J. & Donoso, A. O. (1964). Hypophyso-adrenal regulation of moulting in the toad. General and comparative endocrinology. 4 (5): 473-480. Doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(64)90055-3
Triana, T. M., Henao, L. M., Bernal, M. H. (2013). Comparación ontogénica de la frecuencia de muda en Rhinella marina (Anura, Bufonidae). Iheringia Série Zoologia. 103 (1): 47-50. Doi: 10.1590/S0073-47212013000100007
Uetz, P., Freed, P. Hošek, J. (eds.) (2020). The Reptile Database. http://reptiledatabase.reptarium.cz/species?genus=Anolis&species=tolimensis&search_param=%28%28search%3D%27anolis+tolimensis%27%29%29
Wells, K. D. (2010). The ecology and behavior of amphibians. Chicago-London: University of Chicago Press. p. 1400
Williams, E. E. (1982). Three New Species of the Anolis punctatus complex from Amazonian and inter-Andean Colombia, with comments on the eastern members of the punctatus species group. Breviora. 467: 1-38. Doi: 10.5962/bhl.part.28050
Yanosky, Á. A. & Mercolli, C. (1991). Temperaturas internas y frecuencias de muda en crías de Tupinambis teguixin (Reptilia: Teiidae) bajo condiciones controladas. Cuadernos de Herpetología. 6 (4): 23-26.
Zari, T. A. (1991). The influence of body mass and temperature on the standard metabolic rate of the herbivorous desert lizard, Uromastyx microlepis. Journal of Thermal Biology. 16 (3): 129-133. Doi: 10.1016/0306-4565(91)90033-X

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2020 Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales